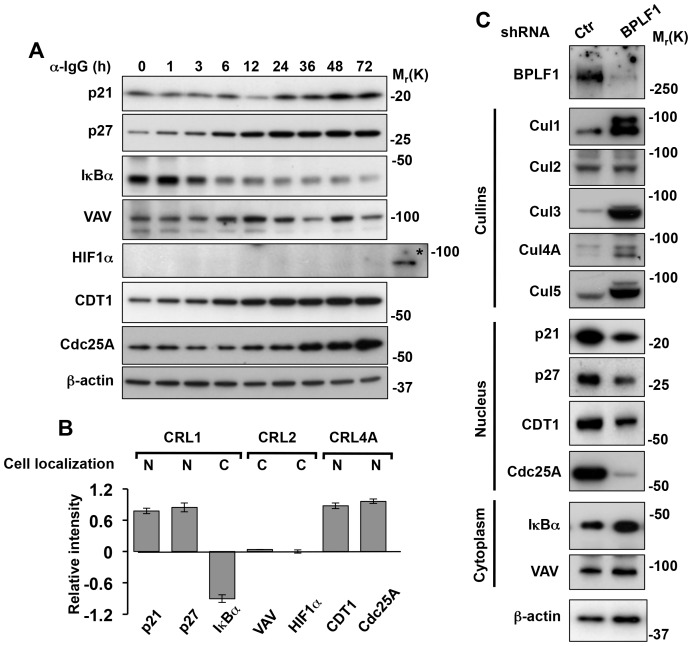
Figure 4. BPLF1 promotes the selective stabilization of nuclear CRL substrates.
The expression levels of nuclear and cytoplasmic CRL substrates were monitored over time in induced Akata-Bx1 cells. A. Representative western blots illustrating the expression levels of CRL1 substrates: p21, p27 and IκBα, CRL2 substrates: VAV and HIF1α, and CRL4A substrates: CDT1 and Cdc25A. The expression level of β-actin is shown as loading control. As control, CRL2 was inactivated by exposing Akata-Bx1 to hypoxia, which resulted in stabilization of HIF1α (indicated by an asterisk). One representative experiment out of three is shown. B. Changes in the expression of nuclear and cytoplasmic CRL substrates in induced Akata-Bx1. The intensity of the specific bands detected at time 0 and after induction for 48 h was quantified. The mean ± SE of the fold change in three independent experiments is shown. C. The selective degradation of nuclear cullins and stabilization of nuclear CRL substrates is dependent on BPLF1. The productive cycle was induced in Akata-Bx1 transfected with a control or BPLF1 specific shRNA and cell lysates collected after 48 h were probed as indicated. One representative experiment out of three where each cullin and CRL substrate was tested is shown.