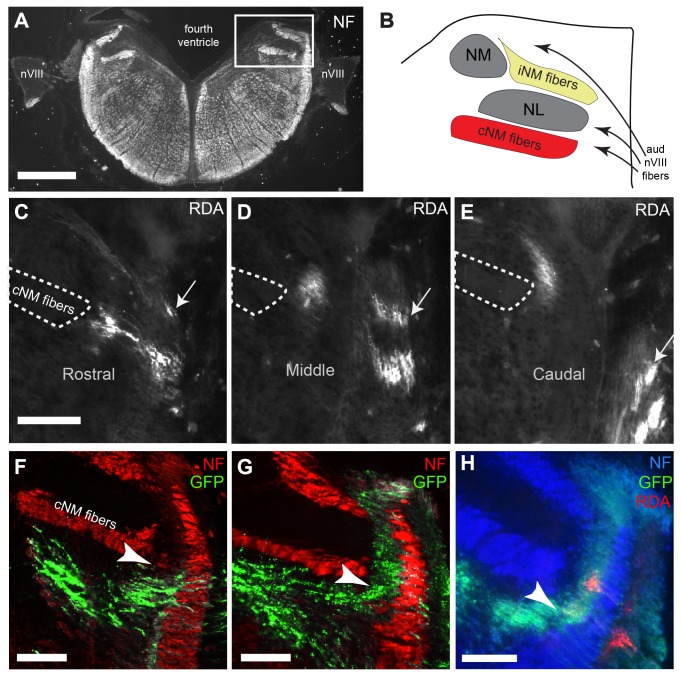
Figure 1. Characterization of auditory and vestibular compartments in the E8 hindbrain.
(A) Low power image of coronal section immunolabeled for neurofilament (NF). The region containing the VIIIth nerve central projections is shown in a rectangle in upper right. Dorsal is up in all all figures. (B) Schematic diagram showing the key features in the boxed region in A. Neurofilament reveals the ipsilateral n. magnocellularis projection (iNM) and the contralateral projection (cNM), seen ventral to n. laminaris (NL). (C-E) Selective labeling of high and low frequency regions of cochlear ganglion cell fibers with RDA reveals the auditory extent of the hindbrain at the level of VIIIth nerve entry. The traced high frequency axons (arrow) are dorsal to the traced lower frequency axons and can be visualized in the hindbrain across several coronal sections (labeled rostral, middle, caudal). (F) Co-staining with neurofilament antibody demonstrates an example in which GFP transfected axons are found only in vestibular ganglion cells. NM-NL fiber tract (cNM fibers, outlined in A-C) acts as a landmark, and is used to demarcate between auditory and vestibular compartments (arrowheads). (G) Example in which both auditory and vestibular ganglion cells are transfected. (H) Embryo with both auditory and vestibular ganglion axons transfected with GFP and subjected to RDA tracing. Central RDA label shows the location of a subset of auditory fibers, which falls within characterized auditory compartment. Scale bars in A, 500 µm; in C (applies to D,E), F, G, and H, 100 µm.