FIGURE 1.
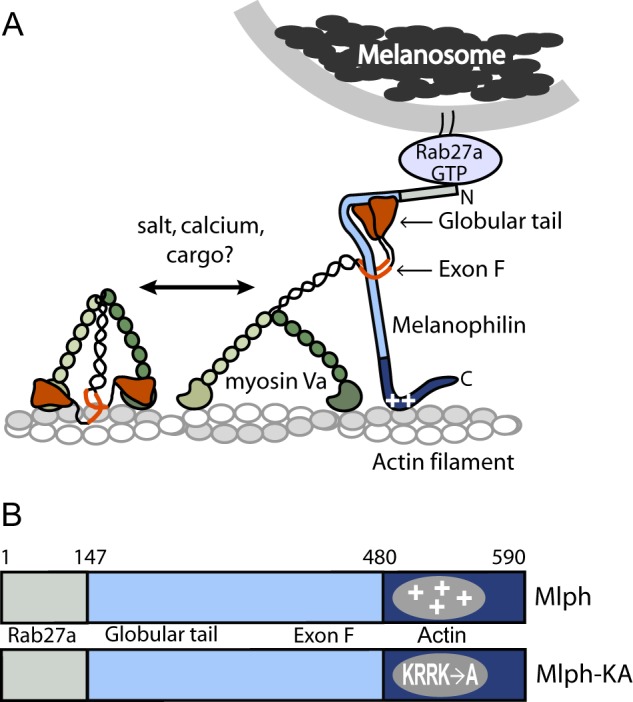
Schematic model of the myoVa-melanosome transport complex and the domain structure of Mlph. A, Mlph linking myoVa to melanosomes via Rab27-GTP. MyoVa exists in an equilibrium between a folded, inhibited state and an extended, active conformation, depending on the ionic strength and calcium concentration in vitro. Binding of cargo has been hypothesized to be the physiologic activator of myoVa. Binding of Mlph to myoVa requires both the globular tail and exon F. Mlph also binds via electrostatic interactions to actin (indicated by plus symbols on Mlph). B, domain structure of Mlph. The N-terminal domain binds to Rab 27a, the intrinsically disordered central portion to myoVa, and the C-terminal region to actin. A mutant Mlph (Mlph-KA) contains four point mutations (K493A/R495A/R496A/K497A) that ablate the positive charge necessary to interact strongly with actin.
