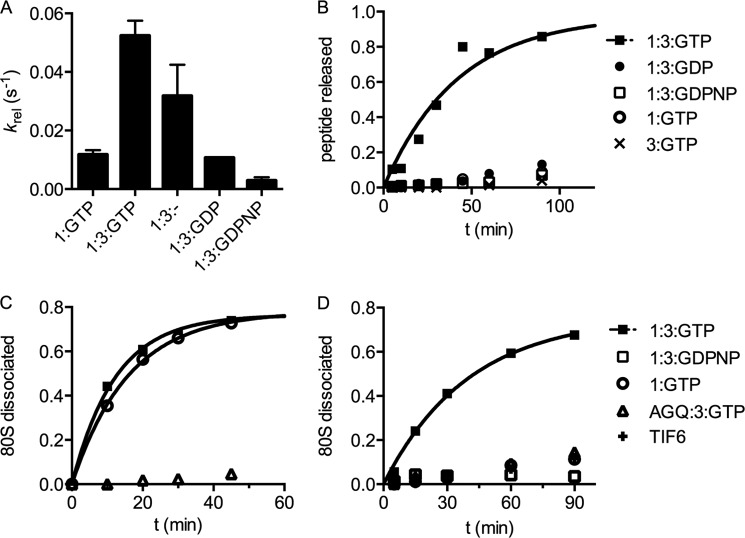
FIGURE 1.
eRF3 markedly stimulates the rate of multiple turnover peptide release by eRF1. A, the rate constant for peptide release at saturating release factor concentrations depends on which factors and nucleotides are added. 1:GTP indicates eRF1 (1 μm) and GTP, 1:3:GTP indicates eRF1, eRF3 (2 μm), and 1 mm GTP, etc. B, multiple turnover peptide release depends on eRF3 and GTP. Limiting (2 nm) eRF1 was incubated with excess pre-termination complex (∼70 nm) and the fraction of dipeptide released was monitored as a function of time. eRF3 was added at saturating levels when indicated; nucleotides were at 1 mm. C, the rate of single turnover subunit dissociation does not depend on eRF3. Termination complexes were prepared with a 32P-labeled tRNA in the P site, and the fraction of subunits dissociated over time was monitored by native gel analysis. Factors were added at saturating concentrations as indicated in the legend. D, multiple turnover subunit dissociation depends on eRF3 and GTP. Termination complexes were prepared as in C and reacted with limiting eRF1, saturating eRF3, and nucleotides as in B.