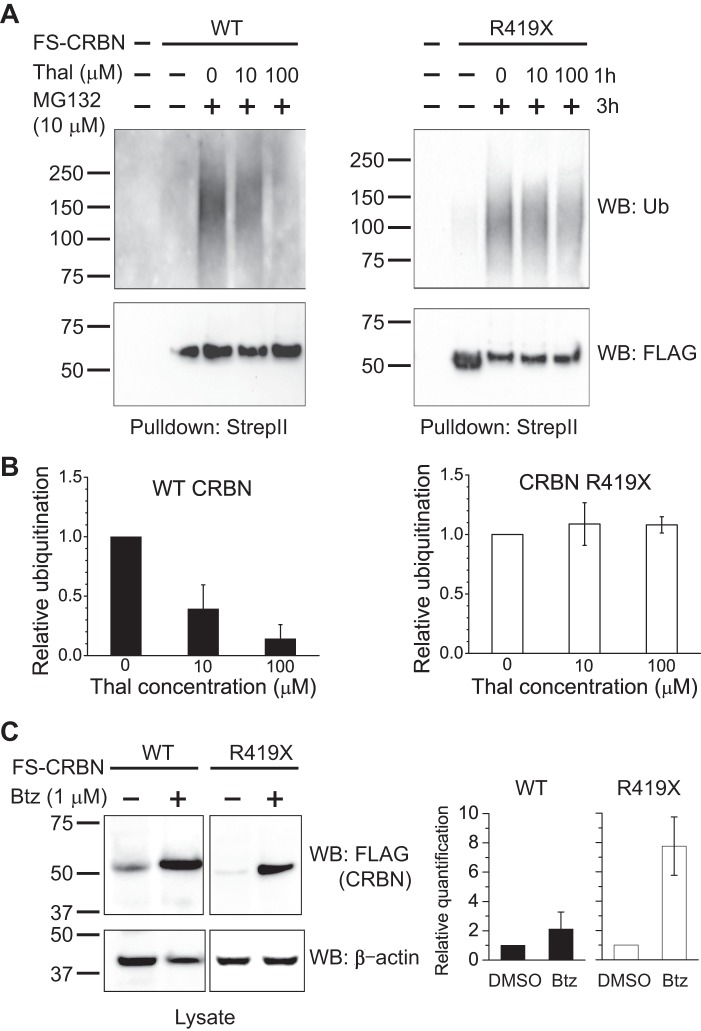
FIGURE 8.
Restoration of CRBN R419X levels by bortezomib. A, thalidomide (Thal) inhibits the ubiquitination of WT CRBN but not CRBN R419X. To test whether thalidomide could block the enhanced autoubiquitination of CRBN R419X, HEK293T cells expressing either WT or R419X CRBN were treated with DMSO, 10 or 100 μm thalidomide for 1 h. Ubiquitinated protein was then allowed to accumulate by treating cells with 10 μm MG132 for 3 h. CRBN was purified with Strep-Tactin beads under denaturing conditions and immunoblotted with anti-ubiquitin or anti-FLAG antibody (loading control). This experiment showed that the ubiquitination level of WT CRBN is reduced by thalidomide treatment, but the ubiquitination level of CRBN R419X was unaffected by thalidomide. B, quantification of the relative ubiquitination level after thalidomide treatment for WT CRBN and R419X mutant. C, clinically utilized proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, significantly increases the cellular level of CRBN R419X. To test whether bortezomib inhibits CRBN degradation, HEK293T cells were transfected with WT and R419X CRBN and treated with DMSO or bortezomib (Btz, 1 μm) for 24 h. Lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, and CRBN levels were determined by immunoblotting with an anti-FLAG antibody. The Western blot (WB) showed that bortezomib slightly increases the protein level of WT CRBN, although it significantly increases the level of CRBN R419X. The right panels show the relative quantification of the WT and R419X CRBN after bortezomib treatment. These data suggest that bortezomib may be useful for restoring CRBN R419X levels in patients with this mutation.