FIGURE 1.
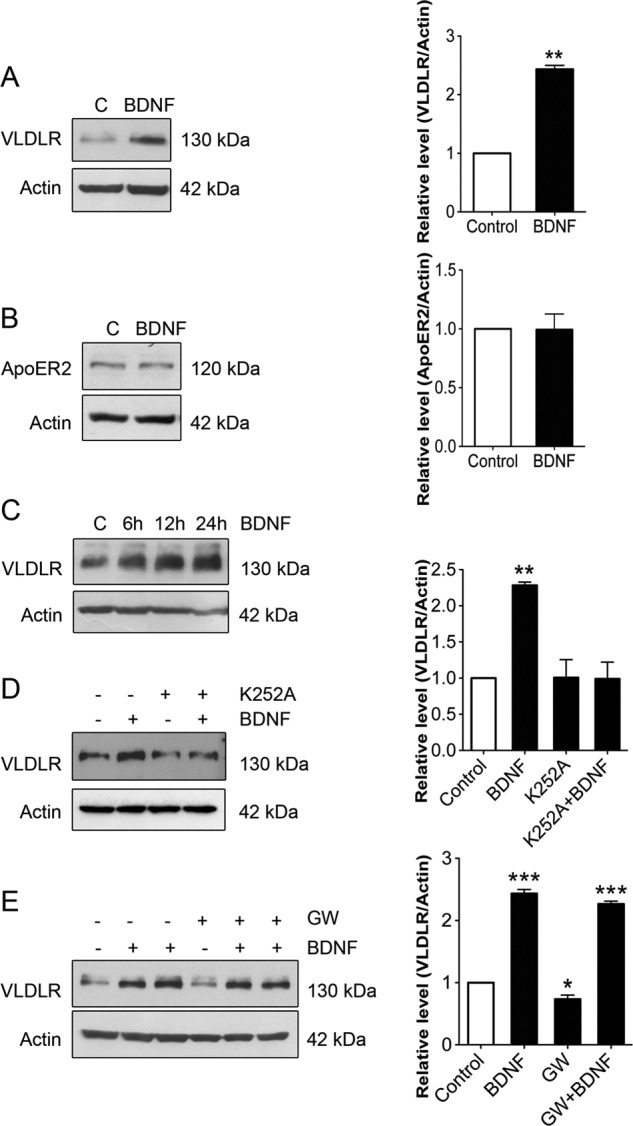
BDNF increases VLDLR levels in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal neurons were prepared from embryonic day 17 rats and cultured for 7 days as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Cells were stimulated with 50 ng/ml BDNF for various times, and immunoblotting was performed using specific antibodies against VLDLR and ApoER2. β-Actin was used as a control. Left panels, immunoblots; right panels, quantifications done using ImageJ. A and B, BDNF added for 24 h significantly increased VLDLR (A) but not ApoER2 (B) levels in hippocampal neurons. Values are means ± S.D. (n = 3). **, p < 0.01 for BDNF versus the control (C). C, time course for the increase in VLDLR by BDNF. A typical immunoblot is shown, and the experiments were repeated three times. D, cells were stimulated with BDNF in the presence of 500 nm K252a to inhibit TrkB receptors. Values are means ± S.D. (n = 3; ANOVA p value, 0.0016; F, 19.92; Tukey's test). **, p < 0.01 for BDNF versus the control. E, the addition of 1 μm GW3965 (GW), which activates LXRs, decreased VLDLR levels in hippocampal neurons, and this was counteracted by co-treatment with BDNF. Values are means ± S.D. (n = 3; ANOVA p value, 0.0001; F, 259; Tukey's test). ***, p < 0.001 for BDNF versus the control and for BDNF + GW3965 versus GW3965; *, p < 0.05 for GW3965 versus the control.
