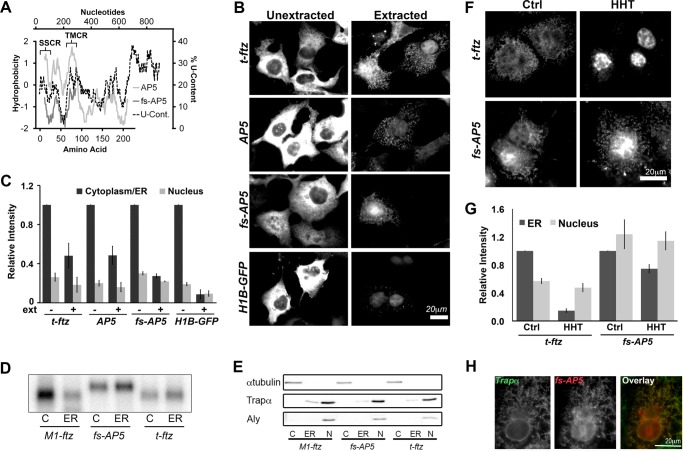
FIGURE 4.
Frameshifted AP5 can still efficiently be maintained on the ER independently of ribosomes and translation. A, hydrophobicity (y axis, left) of the polypeptides encoded by AP5 and fs-AP5 plotted against the peptide length (x axis, bottom). The Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plot was calculated using with a moving window size of 21 amino acids. Note that AP5 encodes the t-ftz signal sequence (residues 1–23 of the AP5 protein), followed by the C-terminal domain of ALPP (including the TMD of ALPP, residues 73–90 of the AP5 protein), and then ends with the hydrophilic ftz protein. In contrast, fs-AP5 does not encode any hydrophobic region. Also note that the frameshift mutation results in the creation of a premature stop codon and a smaller encoded protein. For comparison, the U content (x axis, right) along AP5 (y axis, top) was also plotted. B and C, COS-7 cells transfected with plasmid containing either t-ftz, AP5, fs-AP5, or H1B-GFP and allowed to express mRNA for 18–24 h. Cells were then fixed directly (Unextracted) or first digitonin-extracted (Extracted) and then fixed. Cells were then stained with specific FISH probes (ftz probes were used to for AP5 and fs-AP5) to visualize mRNA distribution. B, representative examples. C, quantification of fluorescence intensities of mRNA in the cytoplasm/ER and nucleus in unextracted (ext−) and extracted (ext+) cells. All data were normalized to the unextracted cytoplasmic/ER staining intensity for each construct. Each bar represents the average ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments (each experiment consisting of n>40 cells). D and E, U2OS cells transfected with plasmid containing either t-ftz, fs-AP5, or M1-ftz. Cytoplasm (C), ER (ER), and nuclear (N) fractions were collected. D, total RNA purified from each fraction. The presence of mRNA was determined via Northern blotting using anti-ftz probes. E, denatured fractions, separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against either Trapα (a resident ER protein), α-tubulin (a cytoplasmic protein), and Aly (a nuclear protein). F and G, COS-7 cells transfected with plasmids containing the t-ftz or fs-AP5 constructs and allowed to express mRNA for 18–24 h. The cells were then treated with DMSO (Ctrl) or HHT for 30 min and then extracted with digitonin. Cells were fixed, stained for mRNA using a FISH probe against ftz, and imaged. F, representative images. G, quantification of the fluorescence intensities of mRNAs in the ER and nucleus. All data were normalized to the ER staining intensity in the control treated group for each construct. Each bar represents the average ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments (each experiment consisting of n>30 cells). H, example of a COS-7 cell expressing fs-AP5 that has been treated with HHT for 30 min and then extracted with digitonin. The cell was co-stained for fs-AP5 using a ftz FISH probe and Trapα, an ER marker, by immunofluorescence. Scale bars, 20 μm.