FIGURE 1.
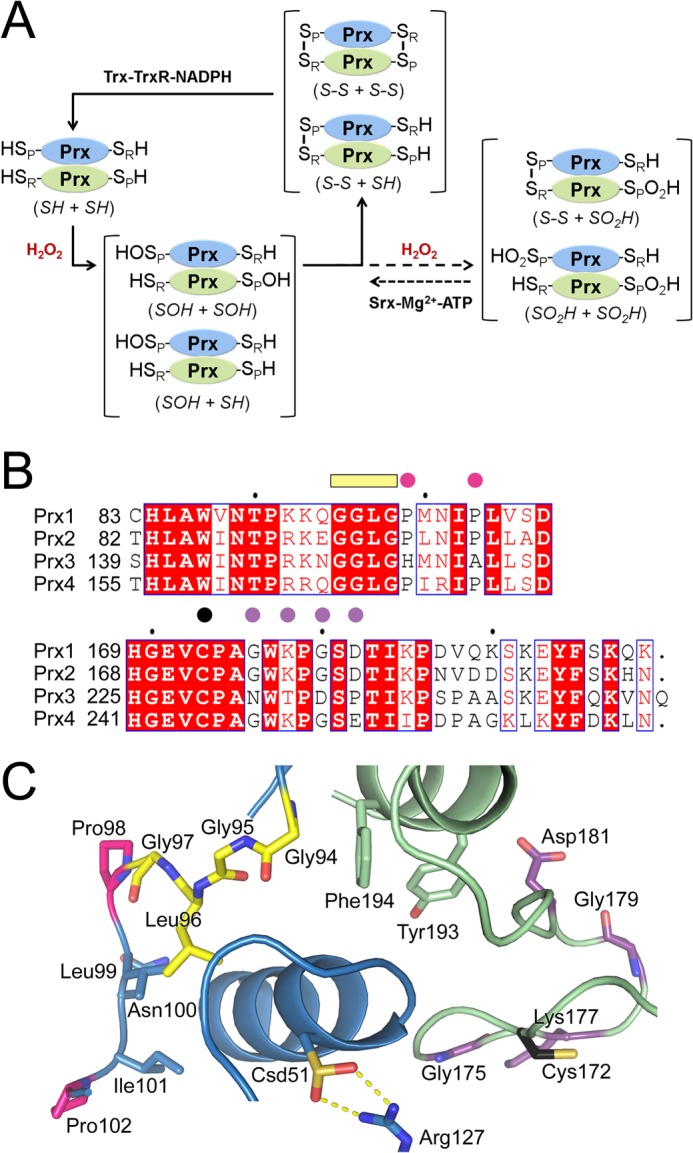
Key residues involved in 2-Cys Prx catalysis and hyperoxidation. A, 2-Cys Prx catalytic cycle showing oxidation, hyperoxidation, and repair by sulfiredoxin. The monomers of the obligate Prx homodimer are shown in blue and green. Depending on the concentration of peroxide present, one or both of the peroxidatic Cys residues (Cys-SPH) may be oxidized to the Cys sulfenic acid (Cys-SPOH) or hyperoxidized to the Cys sulfinic acid (Cys-SPO2H). The resolving Cys residue, Cys-SRH, is located near the C terminus and forms an intermolecular disulfide bond with the Cys-SPH residue during normal catalysis. Reduction of this disulfide and the Cys-SPO2H moiety is performed by the thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase-NAPDH (Trx-Trx-NADPH) system and sulfiredoxin (Srx), respectively. The abbreviation used within the main text for each species is indicated in italics. B, sequence alignment of key residues within the active site. The following motifs and residues are highlighted: GGLG motif, yellow bar; residue differences between the Prxs, pink and purple circles; Cys-SRH residue, black circle. C, active site of hyperoxidized, human Prx2. The same coloring scheme from B is used. The peroxidatic Cys is hyperoxidized and labeled as Csd51. The Cys-SRH residue for Prx2 is Cys-172. PDB code 1QMV (19).
