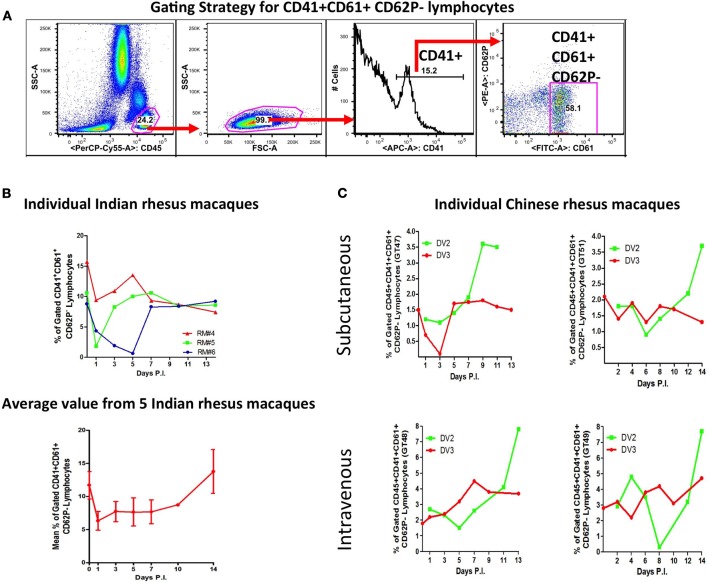
Figure 3.
Dynamics of lymphocyte-platelet aggregates (LymPA) during DV infection. Indian and Chinese rhesus macaques were infected as detailed in Figure 1. In addition, the Chinese macaques were challenged 2 months later with DV3 strain Hawaii. Peripheral blood samples obtained on Days 1 through 14 were subjected to flow cytometric analysis with CD45, CD41, CD61, and CD62P fluorescent antibodies. The frequencies of CD45+CD41+CD61+CD62P− cells over time is graphed. (A) Panels to illustrate the gating strategy employed to analyze lymphocyte-platelet aggregates (LymPA). (B) The kinetics of LymPA in Indian rhesus macaques. The top graph displays LymPA frequencies from 3 individual macaques and the bottom graph, the average population frequency from 5 primates. The LymPA population is down-regulated during DV infection in Indian rhesus macaques. (C) LymPA kinetics in subcutaneously and intravenously infected Chinese rhesus macaques during primary DV2 (green line) and secondary DV3 infection (red line). The frequency of LymPA increases late after primary but not after secondary infection.