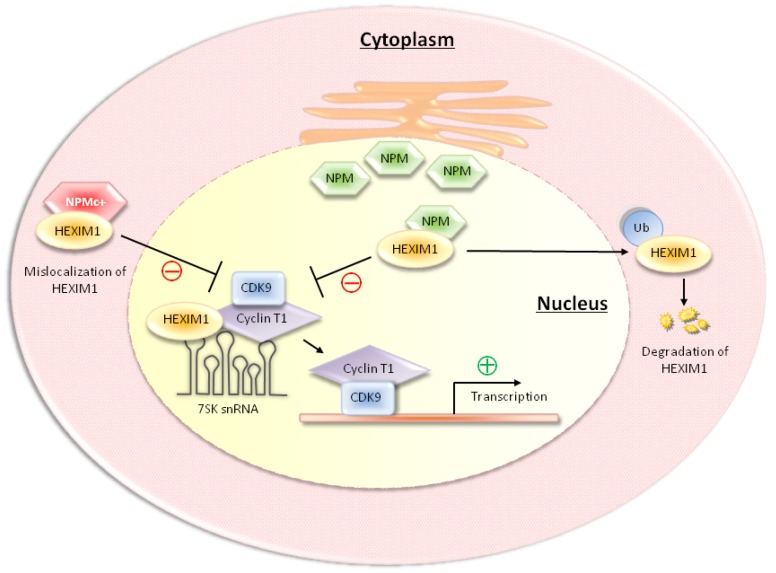
Figure 2.
NPM binds to HEXIM1 and mediates the proteasome-dependent degradation of HEXIM1, which favors the release of the small P-TEFb (i.e., CDK9/cyclin T1) from the HEXIM1-containing large P-TEFb complexes. The cytoplasmic NPM mutant, NPMc+, associates and misallocates a portion of HEXIM1 in cytoplasm, resulting in decreases in the formation of large P-TEFb complexes and activation of RNAP II transcription.