Figure 1.
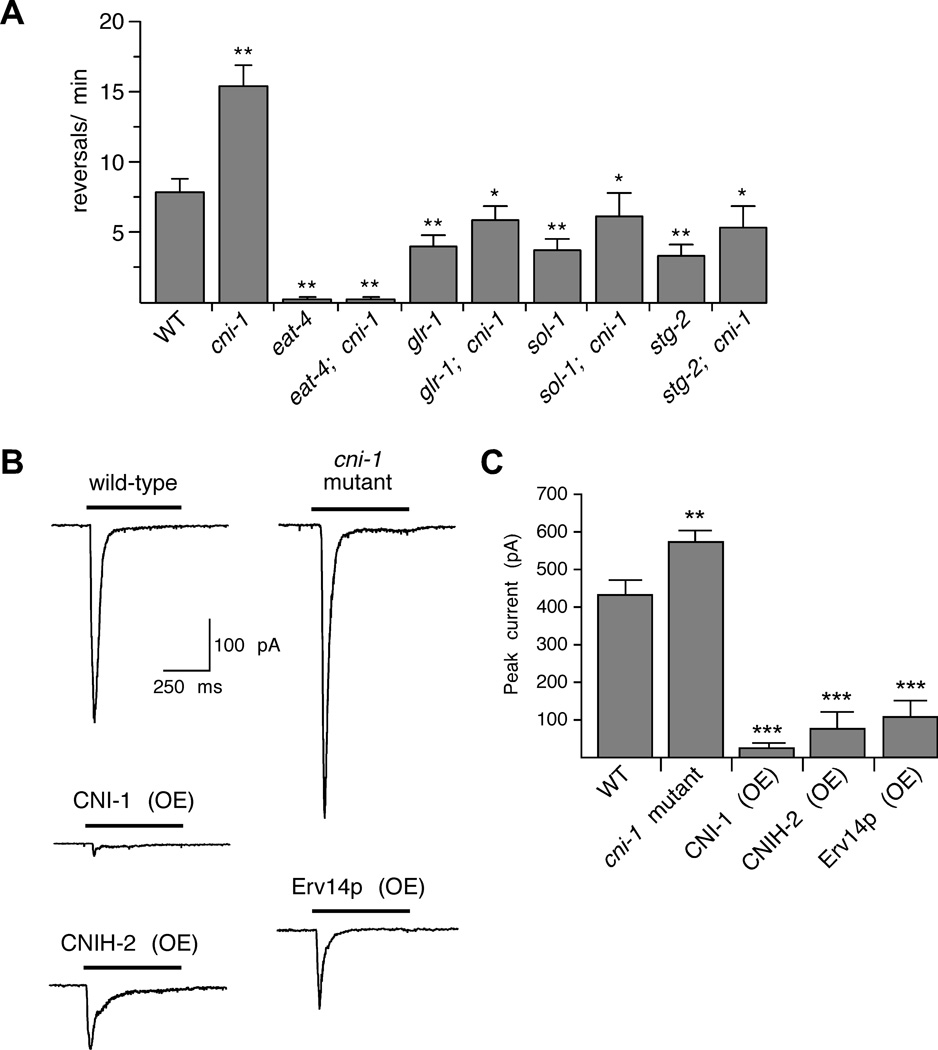
Reversal frequency and glutamate-gated currents are increased in cni-1 mutants. (A) Reversal frequency in wild-type worms and various single and double mutants. For wild-type and cni-1 mutants, n=8; for glr-1,sol-1 and stg-2 single and double mutants, n=7; and for eat-4 single and double mutants, n=5. ** Significantly different from both wild type and cni-1 mutants (p<0.01). * Significantly different from cni-1 mutants (p<0.05). (B) Currents measured in AVA neurons in response to pressure application of 3 mM glutamate. Cells were voltage-clamped at −60 mV. (C) Average peak glutamate-gated current in wild-type worms (n=11), cni-1 mutants (n=11) and transgenic mutants that overexpressed (OE) either CNI-1 (n=6), CNIH-2 (n=8) or Erv14p (n=7). Significantly different from wild type (** p<0.01 and *** p<0.001). Error bars indicate SEM.
See also Figures S1, S2 and S3.