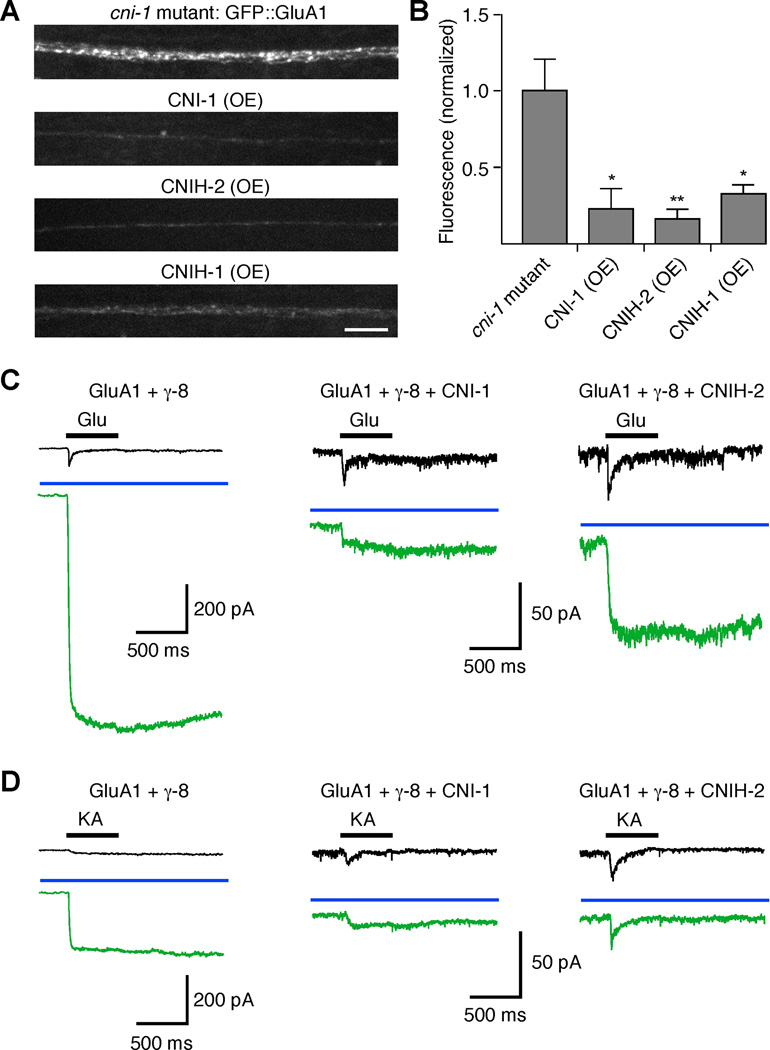
Figure 8.
Reconstitution of vertebrate GluA1 receptor function in transgenic C. elegans. Cornichon proteins decrease GluA1-mediated current and synaptic GluA1 levels when coexpressed in C. elegans AVA neurons. (A and B) Confocal images (A) and quantification (B) of GFP::GluA1 fluorescence in the AVA neurons of transgenic cni-1 mutants (n=9), or transgenic mutants that also overexpressed CNI-1 (n=4), CNIH-2 (n=5) or CNIH-1 (n=5). Scale bar represents 5 µm; error bars represent SEM. Significantly different from cni-1 mutants (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01). (C and D) GluA1-mediated glutamate- (C) and kainate- (D) gated current in the AVA neurons of various transgenic worms both before (black) and after (green) treatment with 100 µM cyclothiazide. The blue bar indicates the presence of cyclothiazide.