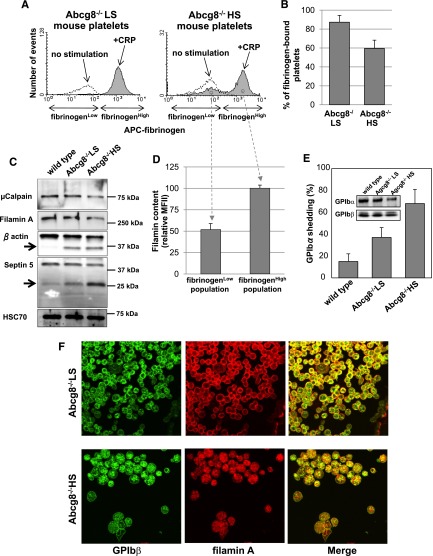
Figure 4.
Decreased fibrinogen binding and increased proteolysis of GPIb and filamin in sitosterolemic platelets. Blood from Abcg8−/− LS and Abcg8−/− HS mice were incubated with 10 μg/mL of collagen-related peptide in the presence of antigen-presenting cell (APC)-labeled fibrinogen for 10 minutes at room temperature. Blood samples were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-FlnA antibody followed by AlexaFluor405-labeled goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G. Note that ∼40% of Abcg8−/− HS platelets failed to bind fibrinogen (A-B). (C) Western blot analysis of platelet lysate confirmed decrease of cellular filamin and other known µ-calpain substrates β actin and septin 5. (D) Analysis of intracellular filamin content by flow cytometry shows selective cleavage and degradation of filamins in the Abcg8−/− HS platelet population that become refractory to agonist stimulation. (E) Surface expression of GPIbα in platelets double stained with PE-labeled anti-mouse αIIb mAb and a mAb specific for the N-terminal 45 kDa domain of GPIbα and analyzed by flow cytometry. GPIbα shedding was expressed as the percentage of GPIbα-negative platelets in total platelets. Inset: western blot analysis of platelets from the same preparation, demonstrating loss of GPIbα from Abcg8−/− HS platelets. (F) Subcellular localization of FlnA in Abcg8−/− HS and Abcg8−/− LS platelets analyzed by confocal microscopy reveals marked reduction in the GPIb/filamin complex from the cell periphery.