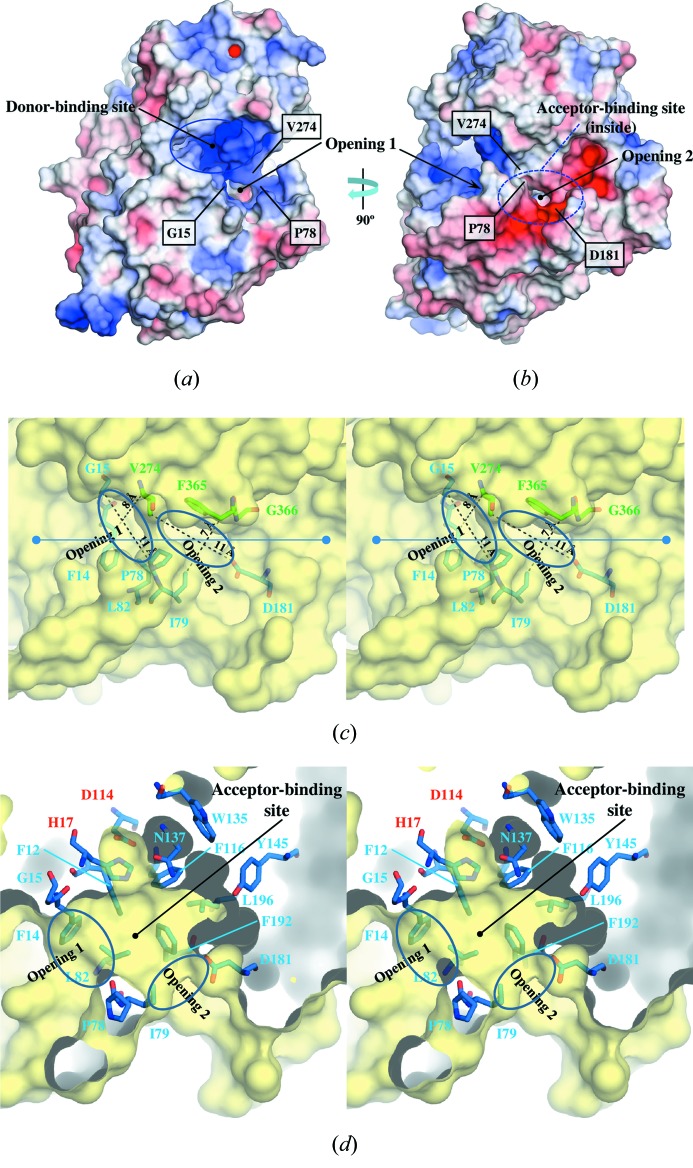
Figure 3.
(a) Electrostatic surface potential of Ct3GT-A viewed from the same direction as in Fig. 2(a) ▶. The surfaces are colored by electrostatic potential isocontours from the potential of +5 kT e−1 (blue) to −5 kT e−1 (red). (b) Electrostatic surface potential of Ct3GT-A after rotating 90° around the vertical axis. (c) Close-up view of the two openings leading to the acceptor-binding site. The residues involved in forming the openings are shown as stick models. The distances showing apparent size of the openings are indicated with dashed lines. (d) Cross-section view of the acceptor-binding site after rotating approximately 45° with respect to the figure (along the line) in (c). The residues involved in forming the acceptor-binding site are shown as stick models. The conserved catalytic residues, His17 and Asp114, are labeled in red.