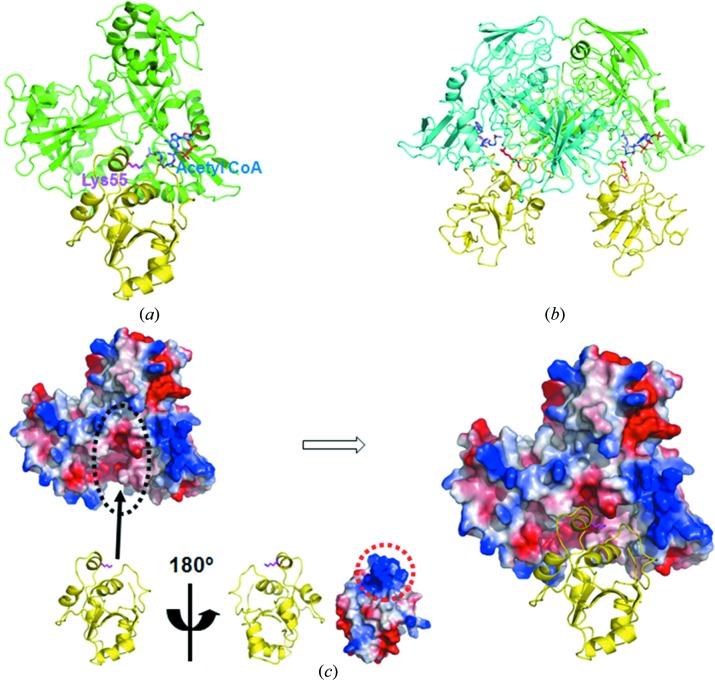
Figure 3.
Docking model of the Mtb Eis monomer with DUSP16/MKP-7. (a) Cartoon docking model of Mtb Eis monomer (PDB code 3ryo: green) and DUSP16/MKP-7 (PDB code 2vsw: yellow). Acetyl-CoA (blue) bound to Eis and Lys55 (magenta) of DUSP16/MKP-7 are shown as a ball-and-stick model. (b) Cartoon docking model of Mtb Eis dimer (PDB code 3ryo: green and cyan) and DUSP16/MKP-7 (PDB code 2vsw: yellow). Acetyl-CoA (blue) bound to Eis and Lys55 (red) of DUSP16/MKP-7 are shown as a ball-and-stick model. (c) The same monomer docking model is presented as an electrostatic surface diagram of Mtb Eis and a cartoon model of DUSP16/MKP-7. A black dotted circle indicates the active binding site of Mtb Eis. Both the cartoon model and electrostatic surface diagram of DUSP16/MKP-7 rotated by 180° are shown on a smaller scale. A red dotted circle indicates the binding site of DUSP16/MKP-7 with positive electrostatic potential. Blue and red colors of the electrostatic surface diagrams correspond to positive and negative electrostatic potentials at neutral pH, respectively.