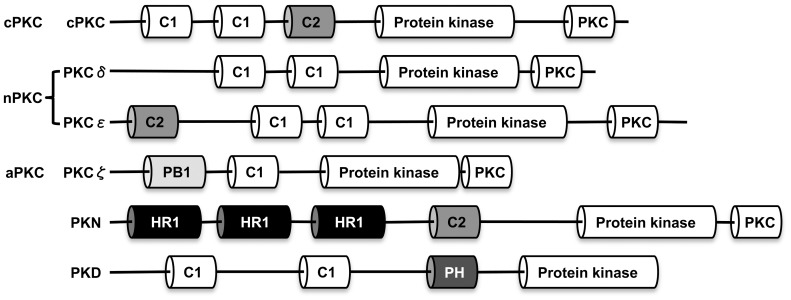
Figure 1. The domain structure of the PKC gene family in Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles stephensi.
Organization of the conserved domains in A. gambiae and A. stephensi PKC gene family. Based on their regulatory domains, PKC family members can be divided into five structurally and functionally distinct subgroups: classical PKCs (cPKC), novel PKCs (nPKC), atypical PKCs (aPKC), PKC-related kinases (PKN) and protein kinase Ds (PKD). Zinc finger-like cysteine-rich motifs (C1) can function to bind diacylglycerol and phospholipids. C2 domains bind phospholipids. Phox/Bem domain 1 (PB1) functions as a dimerization domain. Homology region 1 (HR1) binds small-GTPases and pleckstrin homology (PH) domains bind membrane lipids and can tether PKCs to other proteins.