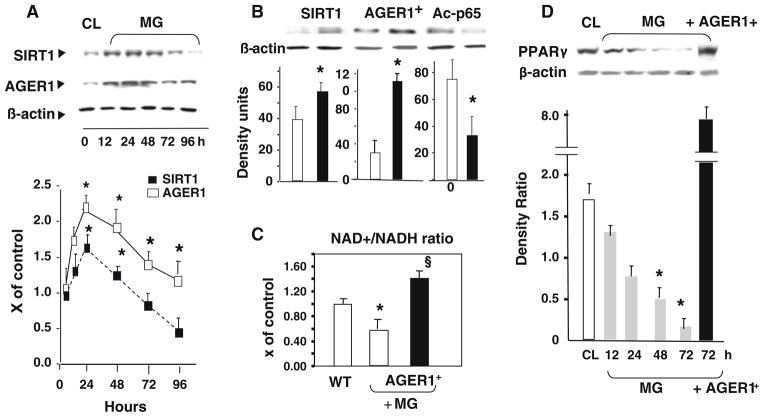
Fig. 4.
Specific AGEs, MG-BSA (MG), modulate SIRT1 and PPARγ expression in THP-1 in vitro. a Time-dependent suppression of SIRT1 protein by MG in vitro parallels that of AGER1. Western blots (upper panels) and densitometry (lower panels) are shown for SIRT1 (black squares) and AGER1 (open squares) in THP-1 cells treated with MG-BSA (60 μg/mL) for up to 96 h. Data on test/β-actin ratios are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 tests). *p < 0.001 vs. non-stimulated cells (CL). b SIRT1 expression and Nf-kB p56 acetylation (Ac-p65) are AGER1-dependent. Wild-type THP-1 cells (WT) or THP-1 cells transfected with AGER1 (AGER1+) were stimulated by MG (60 μg/ mL) for 72 h before Western blots (upper panels) and densitometry plots (lower panels; AGER1+, black bars; WT, open bars). Data (n = 3–5 tests) are shown as mean ± SEM *p <0.001 vs. WT. c MG-induced effects on SIRT1 and ac-p56 are NAD+-dependent and regulated by AGER1. WT or AGER1+ THP-1 cells exposed to MG-BSA (60 μg/mL) for up to 72 h. [NAD+/NADH] ratio is shown as fold (mean ± SEM) above control (n = 3, each in triplicate). *p < 0.001 vs. WT control. §p <0.001 vs. WT treated by MG. d MG suppresses PPARγ protein, but not in cells over-expressing AGER1 (AGER1+). Western blots and density plots, derived from PPARγ/β-actin ratio, are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 4 tests)