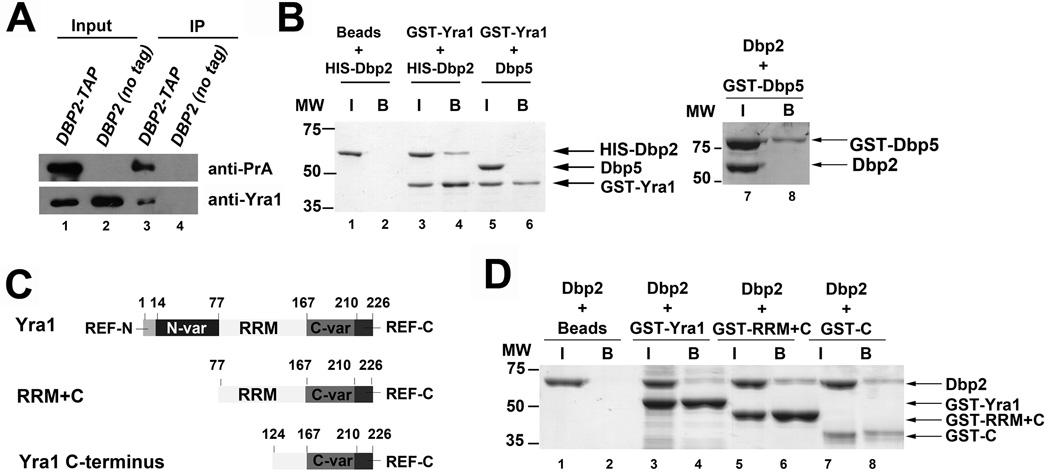
Figure 5. Dbp2 physically interacts with Yra1 in vivo and in vitro.
(A) Yra1 co-immunoprecipitates with Dbp2. Immunoprecipitation assays were performed from wild type (DBP2 no tag) and DBP2-TAP strains using IgG-conjugated dynabeads. 10% lysate was used as input. Proteins from the input and immunoprecipitated fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by Western blotting analysis. (B) Dbp2 interacts directly with Yra1. In vitro pull down assays were performed with recombinant, purified 6XHIS-tagged Dbp2 and GST-tagged Yra1. Briefly, recombinant, purified proteins were incubated together, 20% of the protein mix was removed as input (‘I’) and interacting proteins were selected on glutathione sepharose resin (bound ‘B’ proteins). Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and visualized by Coomassie staining. Neither GST-Yra1 nor Dbp2 co-elute with an unrelated DEAD-box protein Dbp5 (lane 6 and 8), demonstrating that this interaction is specific. (C) Schematic representation of the primary sequence of Yra1, functional motifs and truncation mutants. Yra1 is composed of evolutionarily conserved RNA Export Factor (REF) domains at the N and C terminus separated by variable regions 38; 40; 43; 49. Yra1 also contains a central RNA recognition motif (RRM) that does not appear to harbor RNA binding activity 43 (D) The C-terminal half of Yra1 (aa 124–226) is sufficient to interact with Dbp2. GST-tagged Yra1 and truncation mutants were purified as recombinant proteins from E. coli and subjected to in vitro pull downs as above.