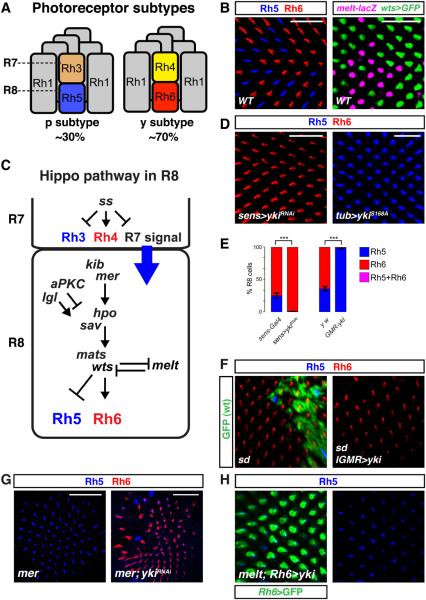
Fig. 1. Yki and Sd instruct mutually exclusive R8 neuron subtypes.
(A) Main photoreceptor subtypes and Rhodopsin coupling in the Drosophila eye.
(B) Confocal images of whole-mounted, wild-type adult retinas. Left: R8 subtypes visualized with antibodies to Rh5 (blue) and Rh6 (red); right: R8 subtypes labeled with transcriptional reporters for melt (β−gal antibody, magenta) and wts (GFP antibody, green). Scale bar, 25μm.
(C) Hippo pathway regulation of R8 subtypes. R7 signals to R8 to induce pR8s (melt and Rh5). yR8 cells express wts and Rh6. wts and melt act in a double negative transcriptional feedback loop. Additional Hippo pathway members required to specify yR8 fate include the entire “core complex” (Wts, the Hpo kinase, the adapter protein Salvador (Sav), and Wts co-factor, Mats) and the upstream regulators Lethal Giant Larvae (Lgl), the FERM-domain protein and NF-2 ortholog, Merlin (Mer), and the WW-domain protein, Kibra (Kib) (4). atypical Protein Kinase C (aPKC) antagonizes yR8 fate. Black arrows and lines represent genetic regulatory interactions.
(D) yki is necessary and sufficient to specify pR8 fate. yki knock-down (ykiRNAi) (left). Pan-photoreceptor expression of activated Yki (right), induced by GMR-flp/FRT mediated excision of a transcriptional STOP between tubulin promoter and ykiS168A (GMR-flp, tub-FRT-STOP-FRT- ykiS168A). Scale bar, 25μm.
(E) Effect of yki manipulations on percentage of R8 cells expressing Rh5 or Rh6 (y-axis). Yki is necessary (left) and sufficient (right) to induce Rh5. Wild-type range is ~20-40% Rh5. From left to right in graph: sens-Gal4 (n=10, N=2998 R8 neurons), sens>ykiRNAi (n=8, N=2112), y,w (n=14 retinas, N=2790), GMR-yki (n=4, N=510). Error bars are ± standard deviation (SD); two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test; ** denotes p < 0.01, *** denotes p <0.001.
(F) sd is required for pR8 fate. Left: sd47M mutant clone (GFP absence). The total number of ommatidia was not reduced, indicating R8 cells were mis-specified into yR8 rather than pR8 cells being lost. Right: Yki mis-expression in sd mutant background.
(G) Yki acts downstream of the Hippo pathway and melt to control Rh5 and Rh6. Left: mer4 (left); right: lGMR>ykiRNAi suppress the mer4 phenotype. Scale bar, 50μm.
(H) Ectopic expression of yki in the opposite subtype with Rh6-Gal4 induces Rh5 in melt?1 mutants. Rh6-Gal4 expressing cells co-labeled by expression of GFP (green). Right: Rh5 channel only. Note: Except where noted, in all manuscript figures Rh5 and Rh6 are labeled in blue (Rh5) and red (Rh6).