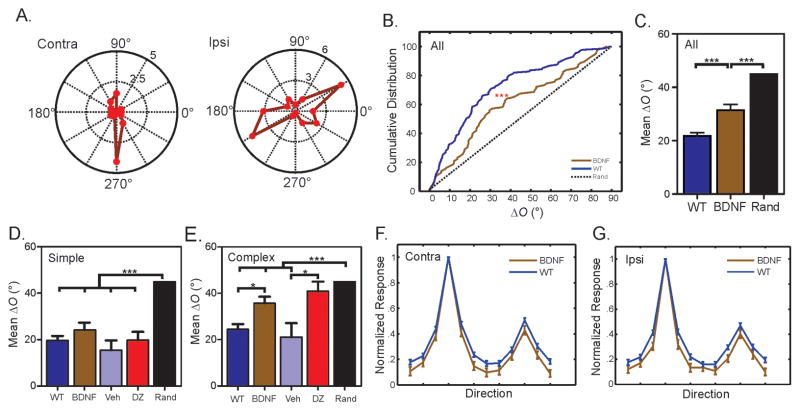
Figure 1. Disrupted binocular matching in mice with precocious critical period plasticity.
(A) Polar plots of orientation tuning curves of a V1 neuron in BDNF-OE mice. The neuron prefers different orientations through the contralateral (“Contra”) and ipsilateral (“Ipsi”) eye. (B) Cumulative distribution of ΔO for WT and BDNF-OE mice. The dotted line represents a uniform distribution if the matching were completely random. (C) Mean ΔO of WT, BDNF-OE mice and random matching (45°). (D) Normal binocular matching in simple cells of BDNF-OE and diazepam-treated WT mice, compared to WT and vehicle controls. (E) Disrupted binocular matching in complex cells of BDNF-OE and diazepam-treated WT mice. (F–G). Mean monocular tuning curves through contralateral (F) and ipsilateral (G) eyes for BDNF-OE and WT mice. Error bars represent mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). See also Figure S1 and Table S1.