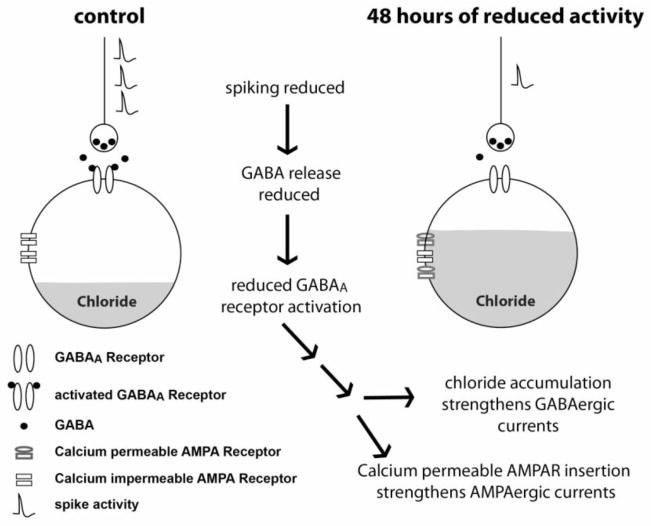
Figure 5.
Model summarizing our current thinking of homeostatic synaptic scaling in embryonic motoneurons following 2-day reductions in spiking activity. Schematic illustrates the concept that reduced spiking activity leads to reduced GABA release, and thereby reduced GABAA receptor activation. 2 days of reduced GABAA receptor activation lead to synaptic scaling through currently unknown pathways. AMPAergic scaling is mediated by the insertion of higher conductance calcium permeable AMPA receptors at the expense of calcium impermeable receptors. GABAergic scaling is mediated by the accumulation of chloride, thereby increasing driving force for GABAA-mediated currents.