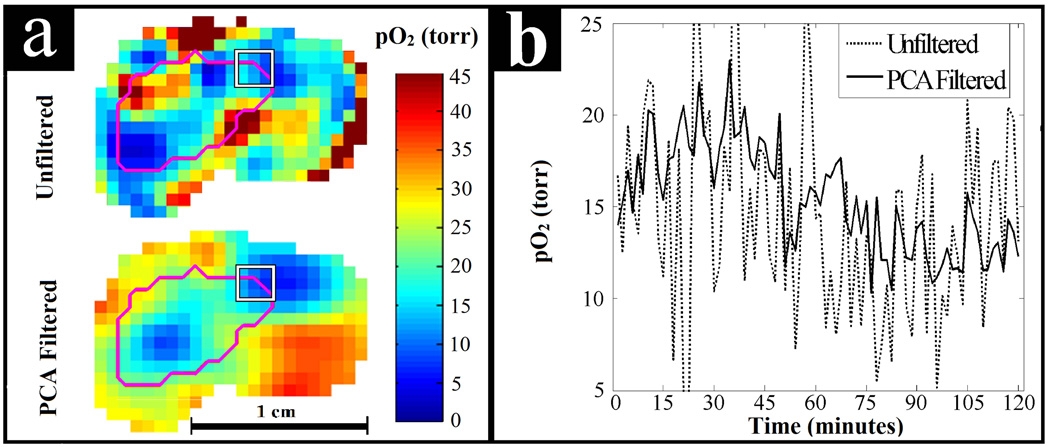
Fig. 9.
PCA filtering applied to a dynamic EPRI study of spontaneous pO2 fluctuations in a murine tumor. (a) Comparison of image quality for unfiltered and PCA filtered pO2 images. The tumor is outlined in magenta and the 27 voxel ROI is outlined by the white square. (b) Observed temporal pO2 fluctuations averaged over the ROI shown on the periphery of the tumor. PCA filtering helps to elucidate apparent sinusoidal pO2 fluctuations that are difficult to discern in the unfiltered data. These fluctuations may be biologically relevant cycling or acute hypoxia.