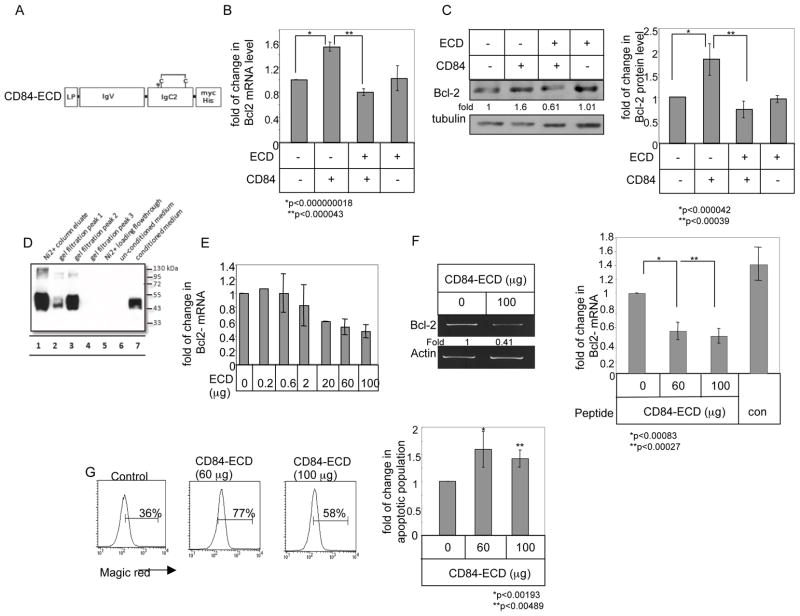
Figure 6.
CD84-ECD blocks the CD84–induced survival cascade in CLL cells. (A) Schematic view of the structure of CD84-ECD. LP-leader peptide, IgV-immunoglobulin domain type V, IgC2- Immunoglobulin domain type C2, TM-transmembrane domain, CD-cytoplasmic domain. N indicates predicted site of N-glycosylation; C indicates disulfide bonds. Length of construct is 330 aa. (B–C) HEK 293 cells were transfected in the presence or absence of empty vector, CD84, or CD84-ECD. (B) Following 18 hours, RNA was purified. Quantitative Real Time PCR was performed using primers for Bcl-2 and RP-2. Results are expressed as the fold change in Bcl-2 expression following the various treatments relative to cells transfected with empty construct, which was defined as 1. The graph summarizes results of four independent experiments with similar results. (C) Cells were lysed 24 hr after transfection, and Bcl-2 and tubulin expression were analyzed by western blot analysis. The graph summarizes results of four independent experiments with similar results. (D) Samples from different purification stages were separated on a 12% gel, and myc expression was analyzed by western blot analysis. Conditioned medium (lane 7) was purified using Ni2+ affinity chromatography (lanes 1 and 5), followed by size exclusion chromatography. Lanes 2–4 shows the peak fraction of the size exclusion chromatography. (E–F) CLL cells were incubated with different amounts of CD84-ECD (E. F) or control (F) proteins. Following 18 h, RNA was purified. RT-PCR and qPCR were performed using primers for Bcl-2 and RP-2. Results are expressed as fold change in Bcl-2 mRNA levels in treated compared to untreated cells, which was defined as 1. The graph summarizes results from three independent experiments with similar results (E), and six (CD84-ECD) and three (Control) independent experiments with similar results (F). (G) CLL cells were incubated with CD84-ECD protein. Following 24h, the cells were stained with Magic Red and analyzed by FACS. The graph summarizes results of five CLL patients.