Figure 2.
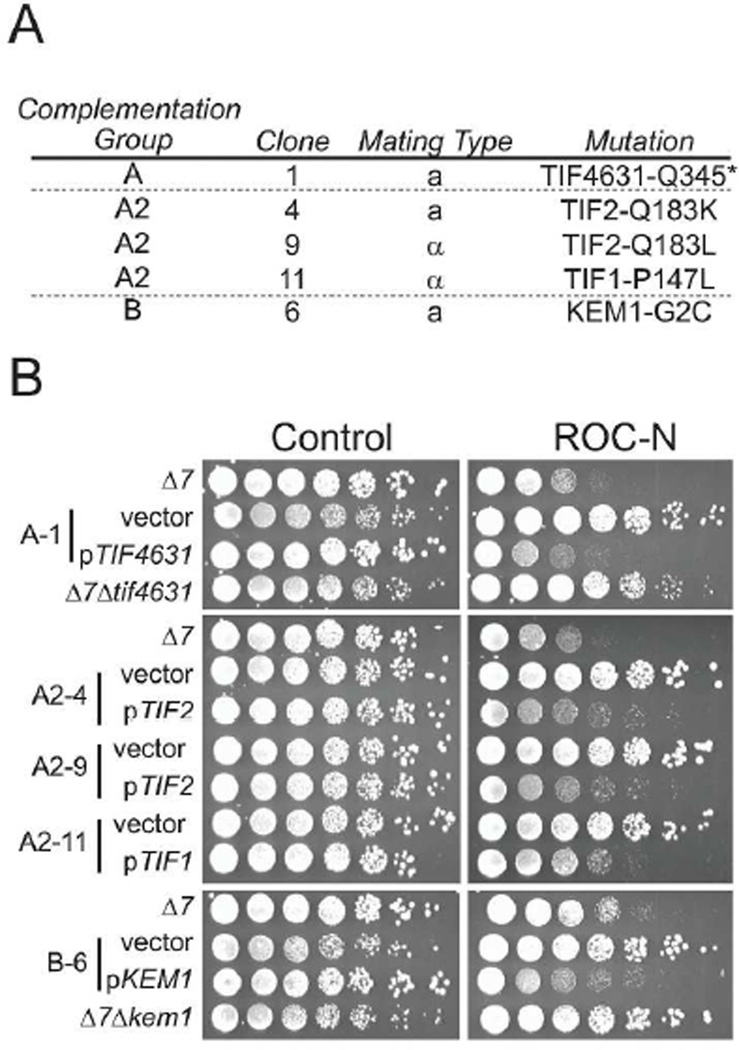
Mutagenesis screening identifies three complementation groups showing resistance to ROC-N. A. Annotation of gene targets found mutated for individual clones within each complementation group. B. Sensitivity of strains from the indicated complementation classes to growth inhibition by ROC-N. Serial dilutions of individual strains were spotted onto minimal media with or without ROC-N (0.7 µM). Note that the parental strain (Δ7) lacks key drug resistance mechanisms, resulting in increased sensitivity to the compound (see Methods). Selected haploid resistant clones demonstrated increased ability to form colonies in the presence of compound as compared to the parental strain. Complementation of the mutant strains with a plasmid-borne (pRS416) wild-type ORF restores compound sensitivity. Replacement of the TIF4631 and KEM1 ORFs in the Δ7 background also leads to increased survival to ROC-N.