Figure 1.
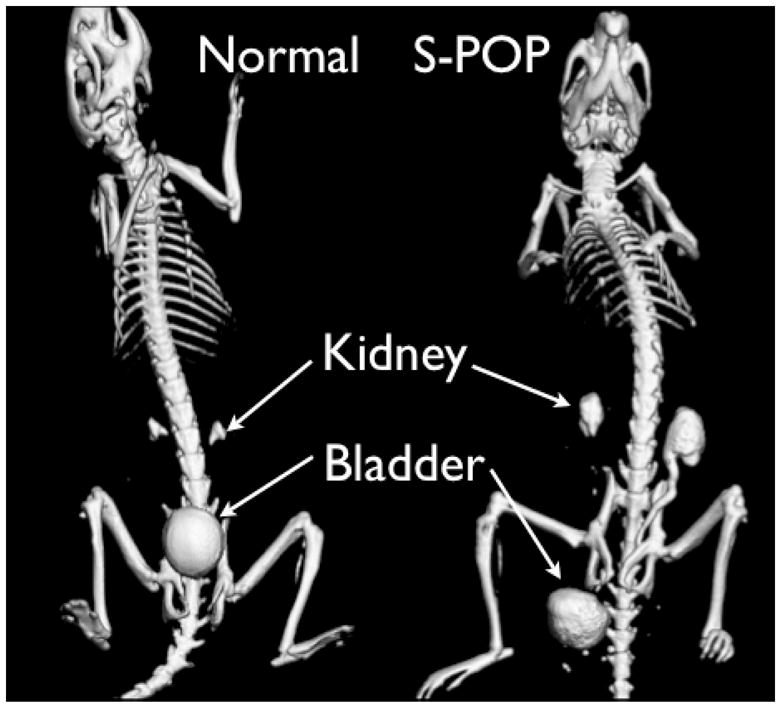
CT images of normal (left) and S-POP male mice (right). The mice were scanned following injection of contrast agent to aid in visualization of the urinary tract. In the normal mouse the smooth spherical object located above the pubic bones is the bladder. Above that, the contrast agent can be seen in the renal pelvi (pyramid shaped objects above the bladder). The bladder in the S-POP mouse is distal to the skeletal pelvis, and the prolapse has resulted in significant retention of contrast agent in the kidneys and ureter, consistent with hydroureter and hydronephrosis.
