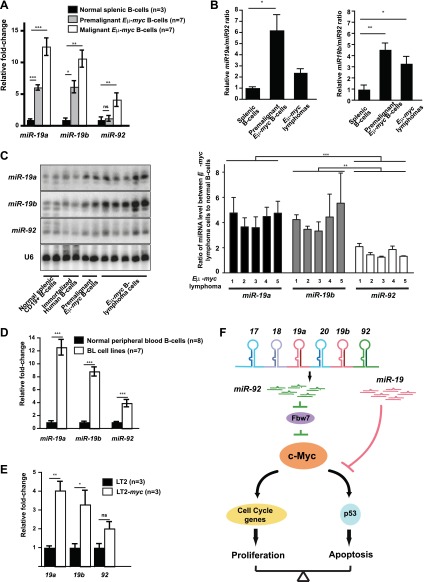
Figure 7. The miR-19:miR-92 antagonism is disrupted during malignant transformation.
(A and B) Compared to normal splenic B-cells, premalignant and malignant Eμ-myc B-cells favored a greater increase in mature miR-19 (miR-19a and miR-19b) than miR-92. The purified normal splenic B-cells, premalignant Eμ-myc bone marrow B-cells and malignant Eμ-myc B-lymphoma cells were subjected to Taqman miRNA assays to determine the expression level of miR-19a, miR-19b and miR-92. Comparing premalignant/malignant Eμ-myc B-cells vs normal splenic B-cells, all three miRNAs exhibited an increased level, although the increase in miR-19a or miR-19b was significantly higher than that of miR-92 (A). In the same experiment, the relative ratios for miR-19a:miR-92 and miR-19b:miR-92 were measured for all normal splenic B-cells and Eμ-myc B-cells (B). (C) Mature miR-19 and miR-92 are differentially expressed in normal splenic B-cells and Eμ-myc B-lymphoma cells. The normal splenic B-cells, immortalized human B-cells, premalignant Eμ-myc/+ B-cells, and Eμ-myc/+ B-lymphoma cells were subjected to Northern analysis. Compared to normal splenic B-cells, both malignant and premalignant Eμ-myc/+ B-cells favored a greater increase of miR-19 than miR-92. (D) Compared to normal B-cells isolated from peripheral blood, human Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines favor a greater increase in mature miR-19 than miR-92. (E) Compared to normal livers (LT2), mouse hepatocellular carcinomas caused by the inducible c-Myc over-expression (LT2-myc) favor a greater increase in mature miR-19 than miR-92. (F) A diagram describes our proposed model to explain the functional interactions between miR-92 and miR-19 in c-Myc-induced B-lymphomagenesis. Aberrant c-Myc expression couples rapid proliferation and p53-dependent apoptosis. miR-92 overexpression further increases c-Myc dosage to strengthen this coupling, at least in part by repressing Fbw7. This miR-92 effect ensures a potent mechanism to eliminate premalignant c-Myc overexpressing cells. Interestingly, miR-92 and can be antagonized by the survival effects of the miR-19 miRNAs encoded by the same mir-17-92 miRNA polycistron. Taken together, while miR-19 miRNAs repressed c-Myc-induced apoptosis to promote the oncogenic cooperation between mir-17-92 and c-Myc, miR-92 exhibits a negative regulation. Thus, the antagonistic interactions between miR-92 and miR-19 confer an intricate crosstalk between proliferation and apoptosis. Error bars represent standard deviation, *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.