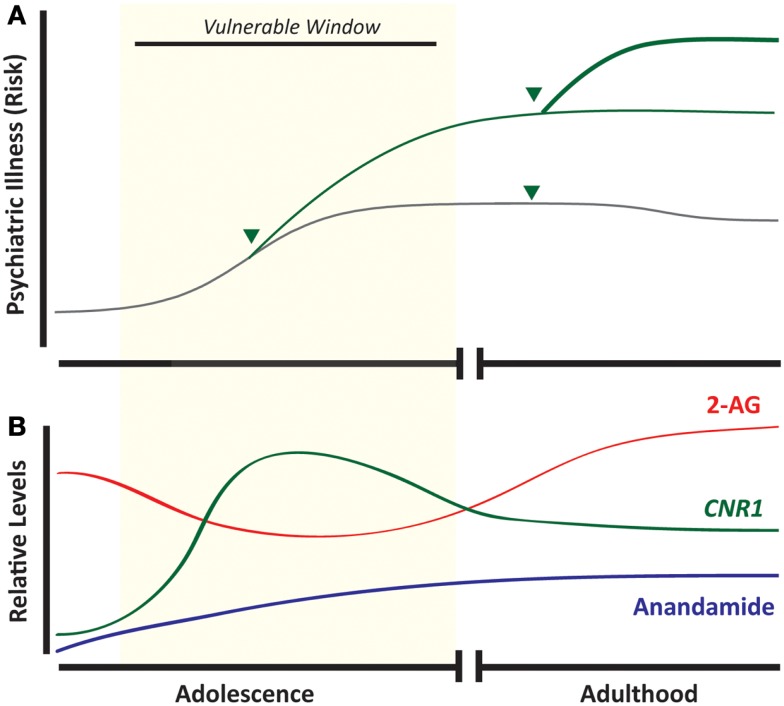
Figure 2.
Developmental cannabis increases vulnerability to psychiatric disease and overlaps with ontogenic changes in the endocannabinoid system. Adolescence is associated with an increased incidence of psychiatric illness, and exposure to cannabis (arrow head) during this developmental window strongly predicts subsequent development of mood disorders, addictive disorders, and schizophrenia (A). Components of the endocannabinoid system appear as early as embryonic life, but maximal CNR1 mRNA expression occurs during adolescence (B). (Green line = cannabis-exposed and gray line = unexposed individuals.)