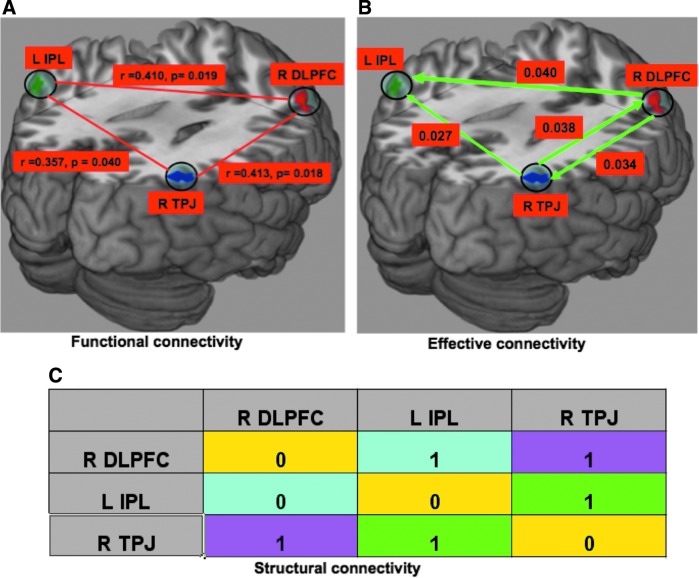
FIG. 5.
Connectivity analysis: (A) Functional connectivity, (B) Directed functional connectivity during audiovisual asynchrony perception by nonparametric Granger causality technique, (C) Structural connectivity based on CoCoMac database (Ghosh et al., 2008; Kotter and Wanke, 2005; Stephan et al., 2000) (“0” means there is no structural connection whereas “1” means there is). Here, r represents the correlation coefficient and p represents significance p-value, the probability of observing the given result by chance if the null hypothesis is true. These three regions are functionally connected (cross-correlation analysis) as shown in plot (A). IPL received the strong causal influences from both TPJ and DLPFC, whereas there was bidirectional causal interaction between them, as shown in plot (B).