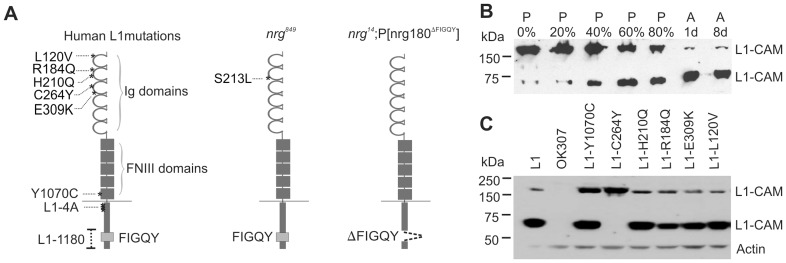
Figure 1. L1-type CAM mutations and their expression in the Drosophila nervous system.
(A) Domain structure of L1CAM showing the locations (asterisks) of different pathological mutations. Mutations L120V, R184Q, H210Q, C264Y, and E309K are in the extracellular Immunoglobulin (Ig) like domains, while Y1070C is in the fifth Fibronectin domain. In the L1-4A protein four amino acids in juxtamembrane region (KGGKYSV) are replaced by alanine residues. The L1-1180 protein lacks part of its C-terminus including the FIGQY motif. The domain structure of Neuroglian (Nrg) indicates the site of the S213L mutation in the second Ig like domain of the nrg849 protein. The genomic pacman P[nrg180ΔFIGQY] rescue construct in the nrg14 null mutant background expresses neuronal Nrg180 that lacks the FIGQY motif. (B) Western blots of pupal stages (in %) and adult (1 and 8 days) flies expressing human UAS-human L1CAM with the OK307 Gal4-driver. Antibodies against the intracellular domain of L1CAM detected 200 kDa and 65 kDa bands. Proteolytic L1CAM cleavage increases with the maturation of the fly nervous system during pupal development and reaches its maximum in the adult. (C) Western blot of transgenic expression of wild-type and mutant UAS-L1 constructs in the wild-type background with the OK307 Gal-4 driver. With an antibody against the intracellular domain of L1CAM a 200 kDa band and 65 kDa band was detected for all L1CAM-constructs except for UAS-L1-C264Y. Only the full length 200 kDa L1CAM form was detected for this construct. No L1CAM protein was detectable in OK307 flies, which served as a negative control. Anti-actin labeling was used as a loading control.