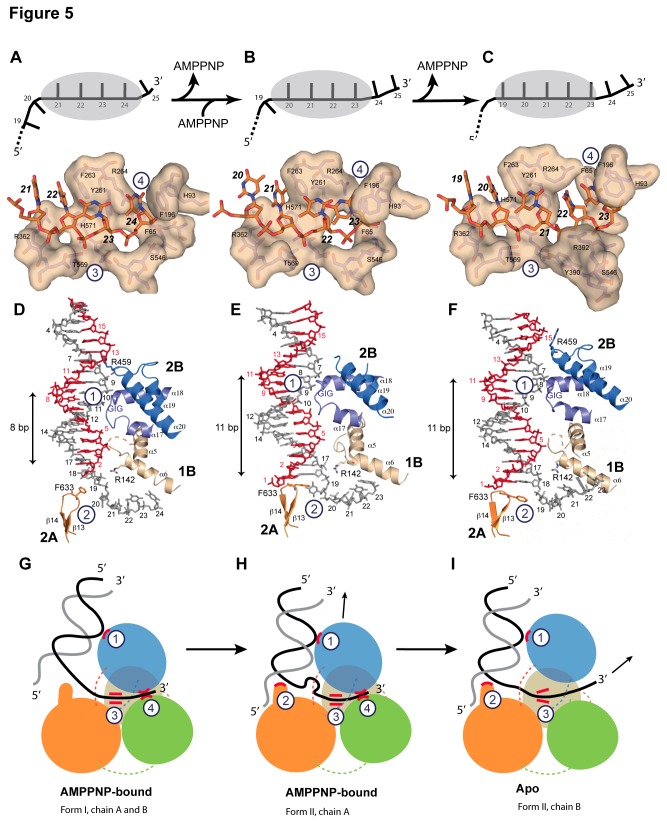
Figure 5. DNA binding of drUvrD.
Illustrations of drUvrD binding to dsDNA with a 3′-ssDNA tail in form I (A,D and G), form II with AMPPNP bound (B, E and H) and in the apo-form of form II (C, F and I). A-C. Schematic diagrams (top) illustrating the translocation of form I (A), form II with AMPPNP bound (B) and the apo-form of form II (C) of drUvrD∆C along the ssDNA. The ssDNA nucleotides are illustrated as black bars and are numbered as in the crystal structures. The grey oval shape representing drUvrD covers the nucleotides bound in the ssDNA binding pocket. Surface representations of the ssDNA binding pockets of these three forms of drUvrD∆C bound to ssDNA (orange sticks) are shown below. The important residues are labeled and the bases are numbered as in the schematic diagrams. D-F. Binding of drUvrD∆C to dsDNA in form I (D), form II with AMPPNP bound (E) and in the apo-form of form II (F). The dsDNA is illustrated in sticks with the translocated strand in grey. Domains of drUvrD are colored as in Figure 2A. The helices belonging to the HLH motifs and the β-hairpin structure (orange) are shown and labeled according to the secondary structure succession (Figure S1). The positively charged residues in contact with dsDNA are illustrated in sticks and the GIG motif is indicated. The number of base-pairs formed between the ss-dsDNA junction and the contact point with the drUvrD GIG motif is shown to the left of each panel. This number differs significantly between the two crystal forms. G-I. Schematic representation of drUvrD's DNA binding in the different crystal structures as indicated below the models. The four protein-DNA contact points that are critical for the wrench-and-inchworm unwinding mechanism are indicated with circled numbers in all panels: HLH motifs interact with dsDNA (1), the β-hairpin motif with the ss-dsDNA junction (2), motif III with the ssDNA (3) and the ssDNA gateway with the exiting ssDNA (4). G. In AMPPNP bound Form I, contact points 1, 3 and 4 are tight. H. In AMPPNP bound Form II, drUvrD's GIG motif (1) has slided along the DNA duplex and pushes the DNA junction against the β-hairpin motif (2), which now stacks tightly against the first base-pair. I. In the apo molecule of Form II, the ssDNA gateway (4) has opened and ssDNA exited the helicase. Domains of drUvrD are colored as in Figure 2A.