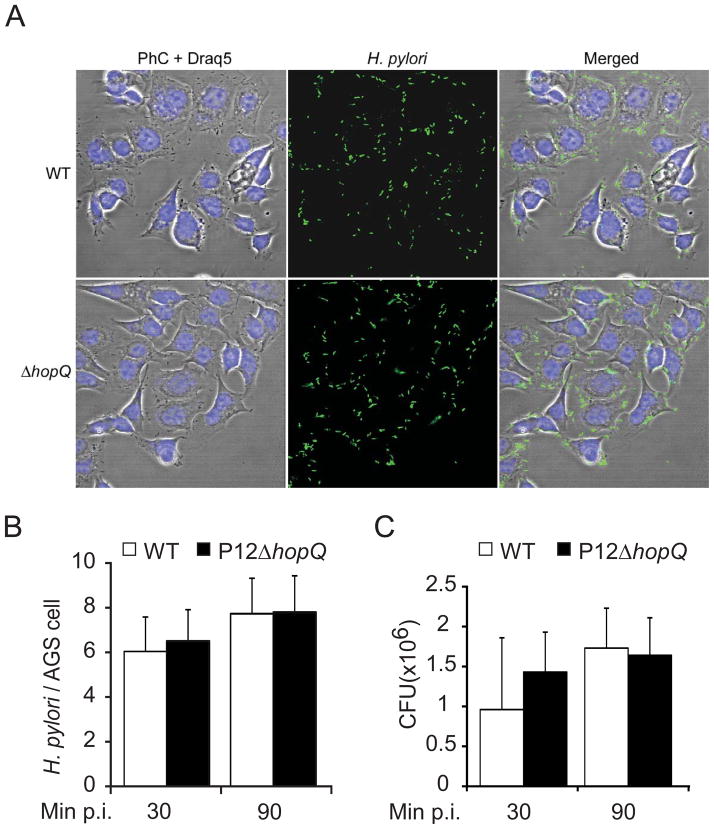
Figure 3. Bacterial adherence to AGS cells is HopQ independent.
(A–C) Adherence of the H. pylori wild type strain P12 (WT) and its mutant (ΔhopQ) to AGS cells. (A) Micrographs of H. pylori (green) attached to AGS cells. Bacteria are visualized by immunofluorescence (green), DRAQ-stained DNA from nuclei and bacterial chromosome (Draq5, blue), and phase-contrast (PhC) (Scale bar, 20 μm. B) Number of adherent bacteria per single AGS cell were enumerated by direct counting through immunofluorescence microscopy. (C) Quantification of CFU after 30 and 90min of infection. Errors bars show standard deviation (± SD) of three independent experiments.