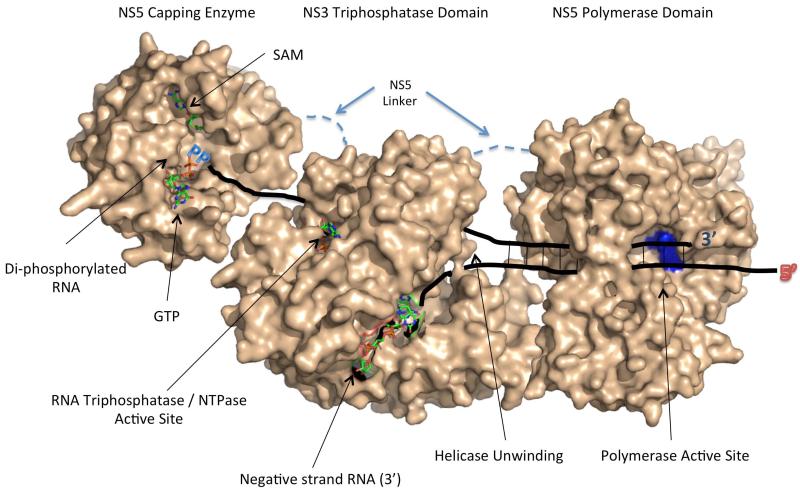
Figure 3. Model for NS3/NS5 Interaction Based on Known Structures and Enzymatic Active Sites.
In this model, the NS3 RNA triphosphatase / helicase domain interacts with NS5 via a flexible linker found between the capping enzyme and RdRP domains (dashed line). The NS3 protease domain is not included in this model for clarity. During positive strand RNA synthesis, the single-stranded negative strand RNA template enters the RdRP active site, and the polymerase catalyzes the elongation of a triphosphorylated positive strand RNA. The positive strand RNA is initially duplexed with the negative strand RNA, and this dsRNA is unwound by the helicase activity present in NS3. The positive strand RNA interacts with the RNA triphosphatase active site, which removes the γ-phosphate from the triphosphorylated RNA, resulting in a di-phosphorylated RNA substrate. The di-phosphorylated RNA is then fed into the NS5 capping enzyme where the guanylyltransferase function caps the RNA and the methyltransferase function methylates the RNA. The model was developed using the following PDB files (NS3 Helicase/RNA Triphosphatase domain (PDB codes: 2 JLR / 2JLU 69, NS5 capping enzyme (PDB Code: 3EVG 66, NS5 RdRP (PDB Code: 2J7U) 90).