Figure 4. Mst2 Autoactivation Is Required for Lats1/2 and YAP Phosphorylation in Human Cells.
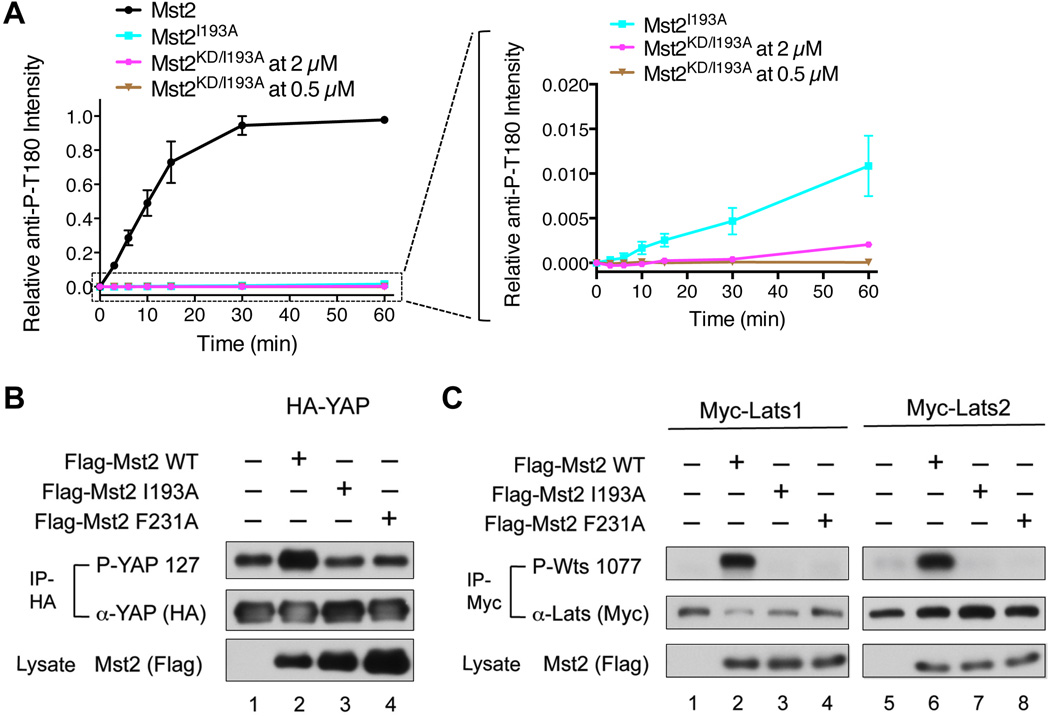
(A) I193A inhibits Mst2 autophosphorylation at T180 even in the context of the full-length Mst2. The kinetics profiles of T180 autophosphorylation of full-length Mst2 (0.5 µM), full-length point mutant Mst2I193A (0.5 µM) and Mst2KD/I193A (2 µM and 0.5 µM) were shown on the left. An enlarged view of the boxed region on the left graph was shown on the right. The full-length Mst2I193A was slightly more efficient than Mst2KD/I193A in autophosphorylation. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. See also Figure S4.
(B) Overexpression of Flag-Mst2 WT, but not the I193A and F231A mutants, enhanced the phosphorylation of HA-YAP. HA-IP from HEK293 cells expressing the indicated constructs was probed with α-phospho-YAP and α-YAP (HA). A fraction of the cell lysate was probed with α-Mst2 (Flag) to evaluate protein expression levels.
(C) Overexpression of Flag-Mst2 WT, but not the I193A and F231A mutants, enhanced the phosphorylation of Myc-Lats1 (left panel) and Myc-Lats2 (right panel). Myc-IP from HEK293 cells expressing the indicated constructs was probed with α-phospho-Wts and α-Myc. A fraction of the cell lysate was probed with α-Mst2 (Flag) to evaluate protein expression levels.