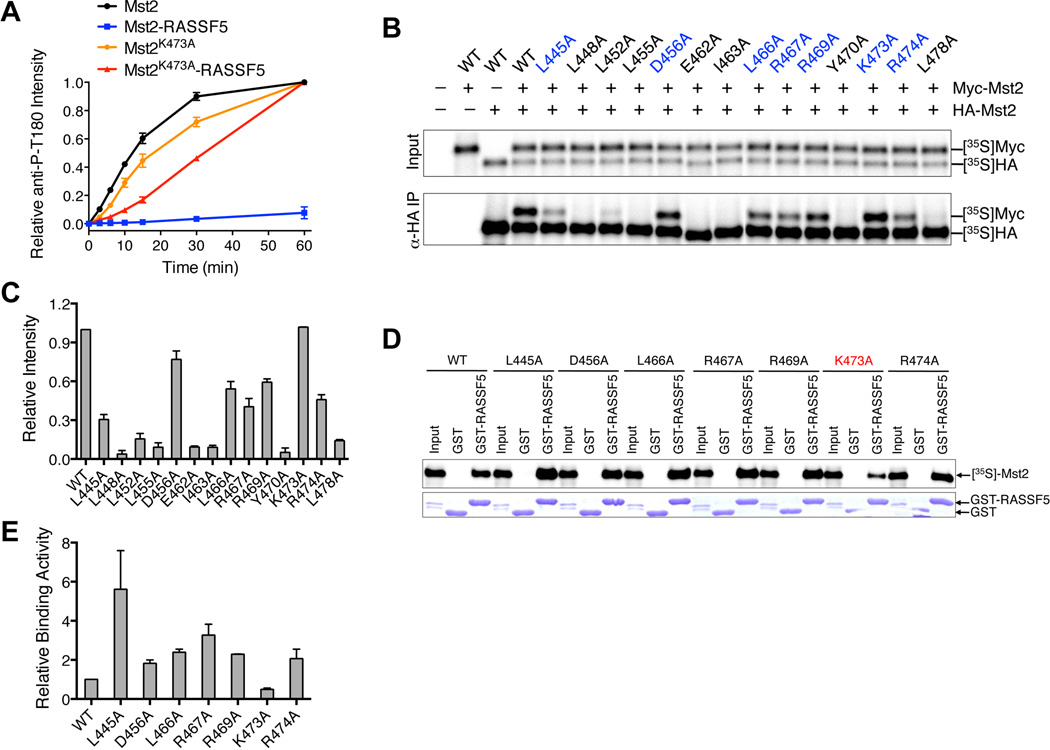
Figure 6. RASSF5 Blocks Mst2 Autoactivation through Heterodimerization.
(A) The kinetic profiles of T180 autophosphorylation of full-length Mst2, the full-length Mst2 and RASSF5-SARAH complex, the full-length point mutant Mst2K473A, and the full-length point mutant Mst2K473A and RASSF5-SARAH complex were shown. The relative α-Mst2 P-T180 intensities were normalized against Mst2 reaction at 60 minute (100%). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.
(B) In vitro dimerization assay of Mst2 mutants. HA- and Myc-tagged Mst2 proteins were co-translated in vitro in the presence of 35S-methionine. The input and anti-HA IP were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed with a phosphor imager. Mutants that retain the dimerization ability were colored in blue.
(C) Quantification of the homodimerization of Mst2 mutants in (B).
(D) Binding between GST-RASSF5-SARAH and in vitro translated Mst2 proteins. Mst2K473A has a weakened interaction with GST-RASSF5 and is labeled in red.
(E) Quantification of GST-RASSF5 binding of Mst2 mutants in (D).