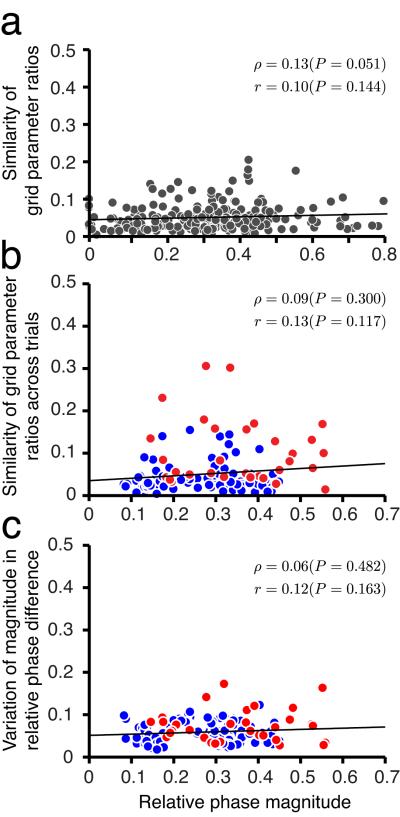
Figure 6.
Stability of cell-cell relationships is independent of distance in spatial phase. (a) Parameters between cell pairs (223 cell pairs from Fig. 1c,d) in the same network are very similar (as reported in Fig. 1), and moreover, the degree of similarity does not vary with the difference in spatial phase (i.e. magnitude of relative phase) between cells (Parameter similarity is defined as the square-root of the squared deviation of parameter ratios from 1, averaged over all parameters per pair). Each dot represents one trial from one cell pair. Black: linear regression; p : Spearman’s rank correlation; r : Pearson’s product-moment correlation. (b) The stability of parameter ratios between cell pairs across rescaling trials (red dots, 7 pairs from Fig. 3f) and novel enclosure trials (blue dots, 24 pairs from Figs. 4 and 5) is independent of the pair’s relative phase. (c) The stability of relative phase (mean of magnitude of relative phase differences) across rescaling and novel enclosure trials is independent of relative phase between cells in a pair (same dataset and color-coding as in b).