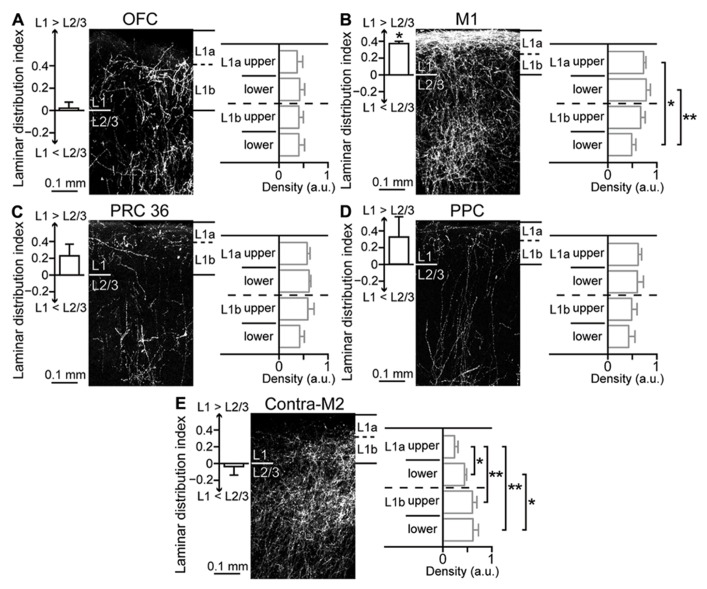
Figure 7.
Laminar pattern of fiber terminations arising from M2 to ipsilateral cortical areas and contralateral M2. (A) M2-derived fiber distributions in L1 and L2/3 of ipsilateral OFC, labeled with BDA-10K injections into L1 to L5 of M2. Left graph, uniform fiber distribution between L1 and L2/3 (P = 0.5, two-tailed one-sample t-test). Laminar distribution index, [(fiber density in L1) - (fiber density in L2/3)]/[(fiber density in L1) + (fiber density in L2/3)], is positive for L1 preference and negative for L2/3 preference. Right graph, uniform fiber distributions along L1, determined by comparing four subdivisions (upper and lower halves of L1a and L1b, respectively). (B) M2-derived fiber distributions in ipsilateral M1. Left graph, denser distribution in L1 than in L2/3 (P < 0.01). Right graph, denser distribution in L1a than in L1b (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; Tukey–Kramer multiple comparisons test). Data taken from Ueta et al. (2013). (C) M2- derived fiber distributions in ipsilateral PRC 36. Left graph, a non-significant trend was observed for denser distribution in L1 than in L2/3 (P = 0.1). Right graph, uniform distributions along L1. (D) M2-derived fiber distributions in ipsilateral PPC, similar to that in ipsilateral PRC 36 (P = 0.15). (E) M2-derived fiber distributions in contralateral M2. Left graph, uniform distribution between L1 and L2/3 (P = 0.53). Right graph, denser distribution in L1b than in L1a (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test).