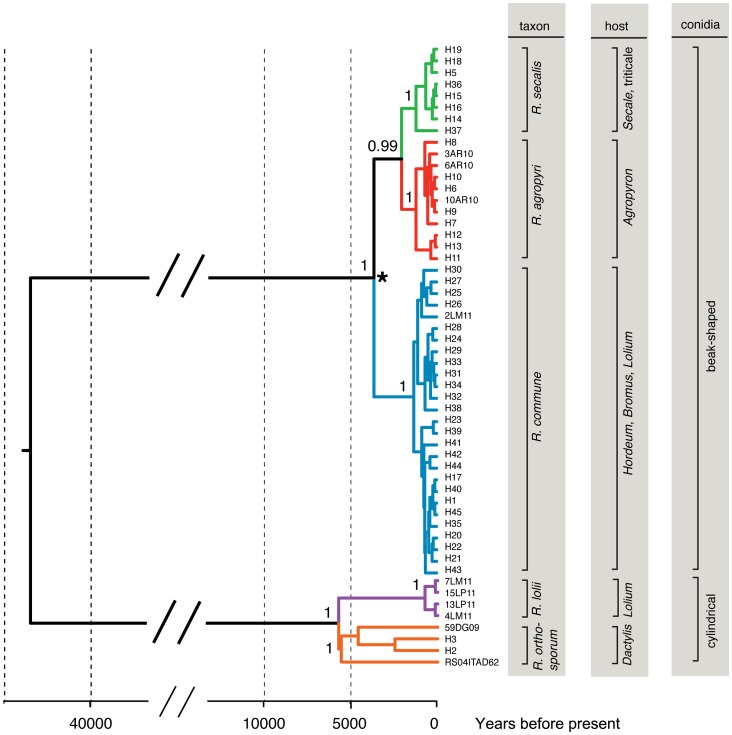
Figure 2. Multilocus phylogeny to determine the evolutionary relationships between five Rhynchosporium species.
Phylogenetic analysis (maximum clade credibility tree) of combined partial sequences of the alpha-tubulin, beta-tubulin and internal transcribed spacer loci show consistent differences between R. commune, R. agropyri, R. secalis, R. orthosporum and R. lolii. Concatenated haplotype (H) sequences sourced from Zaffarano et al. [12] were combined with sequence data obtained from individual isolates in the present study. Posterior probabilities are indicated for major speciation nodes. The asterisk (*) indicates the calibration point used to infer absolute times (ybp; years before present) to the most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) for these Rhynchosporium species (see also Figure S1).