Figure 1.
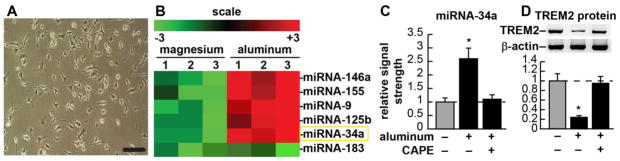
(A) CB-84 (ATCC CRL-2467) murine microglial cells, 32% confluent, phase contrast microscopy; bar = 20 μm; (B) fluorescent-based miRNA array analysis results for 3 magnesium sulfate-treated and 3 aluminum-sulfate-treated experiments using CB-84 murine microglial cells [as described in (A)]; compared to 2 uM ambient magnesium, 2 uM ambient aluminum induces a small family of micro RNAs (miRNAs) in murine microglial cells; these include miRNA-9, miRNA-34a, miRNA-125b, miRNA-146a and miRNA-155 but not miRNA-183; up-regulation of these induced miRNAs has been previously shown to be NF-kB-sensitive [21–23]; microRNAs (miRNAs) are a recently discovered class of single stranded non-coding ribonucleotide regulators which, through base-pair complementarity, bind to the 3′ un-translated (3′-UTR) region of highly selective target mRNAs, and direct the post-transcriptional repression of that mRNA’s encoded genetic information [25,26] (Fig. 1B); the aluminum-mediated up-regulation of miRNA-9, miRNA-146a, miRNA-125b and miRNA-155 and their pathogenic consequences have already been reported [18,20–25,28,33,37]; miRNA-183 is a control miRNA whose levels do not change in the presence of either magnesium or aluminum in microglial or other brain cell types [11,18,22]; (C) Quantitation of fluorescent signals in (B); miRNA-34a (highlighted in a yellow rectangle) is up-regulated 2.6-fold in aluminum-sulfate-treated microglial cells (compared to magnesium sulfate-treated controls); note that treatments longer than 8 hrs with <2 uM ambient aluminum gave quantitatively similar results [23]; addition of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a potent honeybee-resin (propolis)-derived NF-kB inhibitor quenched this induction, indicating the NF-kB-sensitivity of miRNA-34a expression; (D) within the same microglial cells TREM2 protein abundance is shown in comparison to an unchanging control β-actin protein abundance in the same sample; (representative protein bands, upper panel; quantified in bar format, lower panel); TREM2 is significantly down-regulated to 0.24-fold of control values; again, addition of CAPE inhibitor quenched this induction, indicating that TREM2 up-regulation is NF-kB-sensitive. An aluminum-induced reduction in TREM2 expression may therefore impair phagocytosis of Aβ42 peptides with amyloidogenic effects (see text); a dashed horizontal line at 1.0 indicates in (C) control miRNA-34a levels or (D) control TREM2 protein levels for ease of comparison; figures were generated using Adobe Photoshop v9.0 (Adobe, San Jose CA, USA); statistical procedures were analyzed using a two-way factorial analysis of variance (p, ANOVA) and the SAS language (Statistical Analysis Institute, Cary NC, USA) [11,21]. Only p-values less than 0.05 (ANOVA) were considered as statistically significant; N=5, significance over controls *p<0.05 (ANOVA).
