Fig. 1.
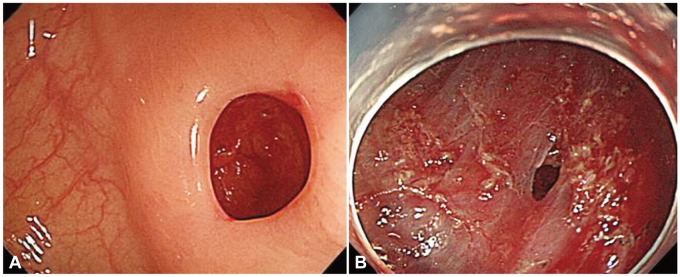
Endoscopically proven perforation. (A) Diagnostic colonoscopy-associated perforation. The perforation occurred during excessive pushing of the colonoscope. It is relatively large. (B) Therapeutic colonoscopy-associated perforation. The perforation developed during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of colonic adenoma. It is relatively small and the surrounding area shows ESD ulcer.
