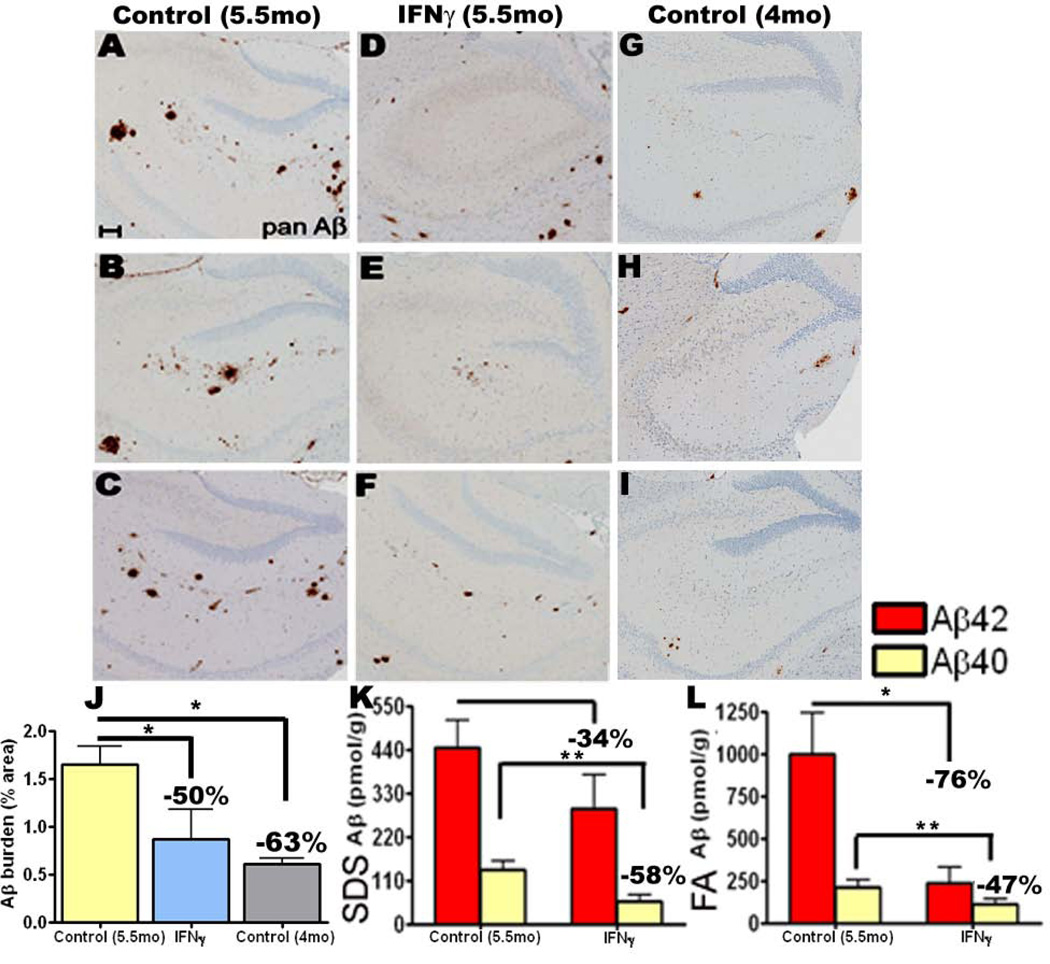
Fig 3. Amyloid deposition is suppressed following acute focal expression of mIFNγ in the hippocampus of TgCRND8 mice.
A-I. 4 month old TgCRND8 mice were stereotaxically injected in the hippocampus with either rAAV1-mIFNγ or rAAV1-EGFP and sacrificed after 6 weeks. Representative brain sections stained with pan Aβ antibody depict attenuation of Aβ deposition in mIFNγ expressing mice (D-F) compared to EGFP injected controls (A-C) in the immediate vicinity of the injection site. Unmanipulated 4 month old TgCRND8 brains, dissected at the same level, are depicted (G-I). Scale Bar, 150µm. n=5/group.
J. Aβ plaque burden analysis shows a significant decrease in amyloid deposition in 5.5 month old mIFNγ expressing mice compared to EGFP expressing age-matched control mice but no change compared to unmanipulated 4 month old TgCRND8. (n=5/group, *p<0.05).
K-L. Biochemical analyses of Aβ42 and Aβ40 levels by ELISA show significant reductions in both SDS-soluble (H) and SDS-insoluble FA fractions (I) in mIFNγ expressing mice compared to controls (n=5/group, *p<0.05 and **p<0.05).