Abstract
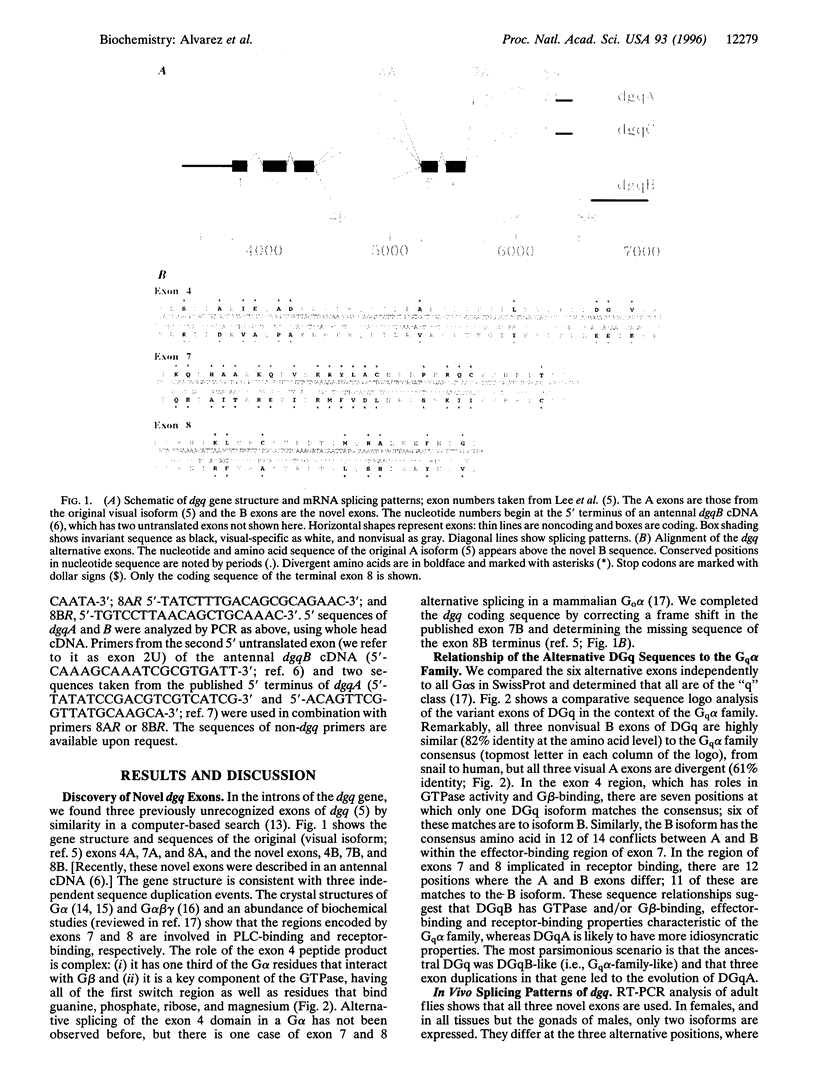
DGq is the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric GTPase (G alpha), which couples rhodopsin to phospholipase C in Drosophila vision. We have uncovered three duplicated exons in dgq by scanning the GenBank data base for unrecognized coding sequences. These alternative exons encode sites involved in GTPase activity and G beta-binding, NorpA (phospholipase C)-binding, and rhodopsin-binding. We examined the in vivo splicing of dgq in adult flies and find that, in all but the male gonads, only two isoforms are expressed. One, dgqA, is the original visual isoform and is expressed in eyes, ocelli, brain, and male gonads. The other, dgqB, has the three novel exons and is widely expressed. Remarkably, all three nonvisual B exons are highly similar (82% identity at the amino acid level) to the Gq alpha family consensus, from Caenorhabditis elegans to human, but all three visual A exons are divergent (61% identity). Intriguingly, we have found a third isoform, dgqC, which is specifically and abundantly expressed in male gonads, and shares the divergent rhodopsin-binding exon of dgqA. We suggest that DGqC is a candidate for the light-signal transducer of a testes-autonomous photosensory clock. This proposal is supported by the finding that rhodopsin 2 and arrestin 1, two photoreceptor-cell-specific genes, are also expressed in male gonads.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R. Olfaction in Drosophila: from odor to behavior. Trends Genet. 1996 May;12(5):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(96)10015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Man-Son-Hing H., Yarfitz S., Colley N. J., Deer J. R., Spencer M., Hurley J. B., Zuker C. S. An eye-specific G beta subunit essential for termination of the phototransduction cascade. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):59–61. doi: 10.1038/370059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Ranganathan R., Colley N. J., Hardy R. W., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Arrestin function in inactivation of G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in vivo. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1910–1916. doi: 10.1126/science.8316831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. C., Inoue H., Yoshioka T., Hotta Y. Quantitative tissue isolation from Drosophila freeze-dried in acetone. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):97–104. doi: 10.1042/bj2430097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebultowicz J. M., Riemann J. G., Raina A. K., Ridgway R. L. Circadian system controlling release of sperm in the insect testes. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1098–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4922.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C. Tripping along the trail to the molecular mechanisms of biological clocks. Trends Neurosci. 1995 May;18(5):230–240. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93908-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C. A histamine-activated chloride channel involved in neurotransmission at a photoreceptor synapse. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):704–706. doi: 10.1038/339704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin P. E. Analysis of period mRNA cycling in Drosophila head and body tissues indicates that body oscillators behave differently from head oscillators. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7211–7218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde D. R., Mecklenburg K. L., Pollock J. A., Vihtelic T. S., Benzer S. Twenty Drosophila visual system cDNA clones: one is a homolog of human arrestin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1008–1012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., McKay R. R., Miller K., Shortridge R. D. Multiple subtypes of phospholipase C are encoded by the norpA gene of Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14376–14382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambright D. G., Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. Structural determinants for activation of the alpha-subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):621–628. doi: 10.1038/369621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambright D. G., Sondek J., Bohm A., Skiba N. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):311–319. doi: 10.1038/379311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. J., Dobbs M. B., Verardi M. L., Hyde D. R. dgq: a drosophila gene encoding a visual system-specific G alpha molecule. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90349-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. J., Shah S., Suzuki E., Zars T., O'Day P. M., Hyde D. R. The Drosophila dgq gene encodes a G alpha protein that mediates phototransduction. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1143–1157. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Gillette M. U. Cholinergic regulation of the suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian rhythm via a muscarinic mechanism at night. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan 15;16(2):744–751. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-02-00744.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mismer D., Michael W. M., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the promoter of the Rh2 opsin gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):173–180. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):654–663. doi: 10.1038/366654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. R. GTP-binding proteins 1: heterotrimeric G proteins. Protein Profile. 1995;2(3):167–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. A., Benzer S. Transcript localization of four opsin genes in the three visual organs of Drosophila; RH2 is ocellus specific. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):779–782. doi: 10.1038/333779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. A., Benzer S. Transcript localization of four opsin genes in the three visual organs of Drosophila; RH2 is ocellus specific. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):779–782. doi: 10.1038/333779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Malicki D. M., Zuker C. S. Signal transduction in Drosophila photoreceptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:283–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesgo-Escovar J., Raha D., Carlson J. R. Requirement for a phospholipase C in odor response: overlap between olfaction and vision in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison K., Gilbert W., Church G. M. Large scale bacterial gene discovery by similarity search. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):205–214. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryba N. J., Findlay J. B., Reid J. D. The molecular cloning of the squid (Loligo forbesi) visual Gq-alpha subunit and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):333–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2920333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stephens R. M. Sequence logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6097–6100. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K., Becker A., Sun Y., Hardy R., Zuker C. Gq alpha protein function in vivo: genetic dissection of its role in photoreceptor cell physiology. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Shieh B. H., Zuker C. S. Isolation and structure of an arrestin gene from Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1003–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker R. F. The organization of the chemosensory system in Drosophila melanogaster: a review. Cell Tissue Res. 1994 Jan;275(1):3–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00305372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talluri S., Bhatt A., Smith D. P. Identification of a Drosophila G protein alpha subunit (dGq alpha-3) expressed in chemosensory cells and central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11475–11479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Wu R. Structure of two unlinked Drosophila melanogaster glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8220–8228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]