Fig. 5. Two xMELK subpopulations have distinct requirement for cell–cell contacts for their localization at the cell cortex.
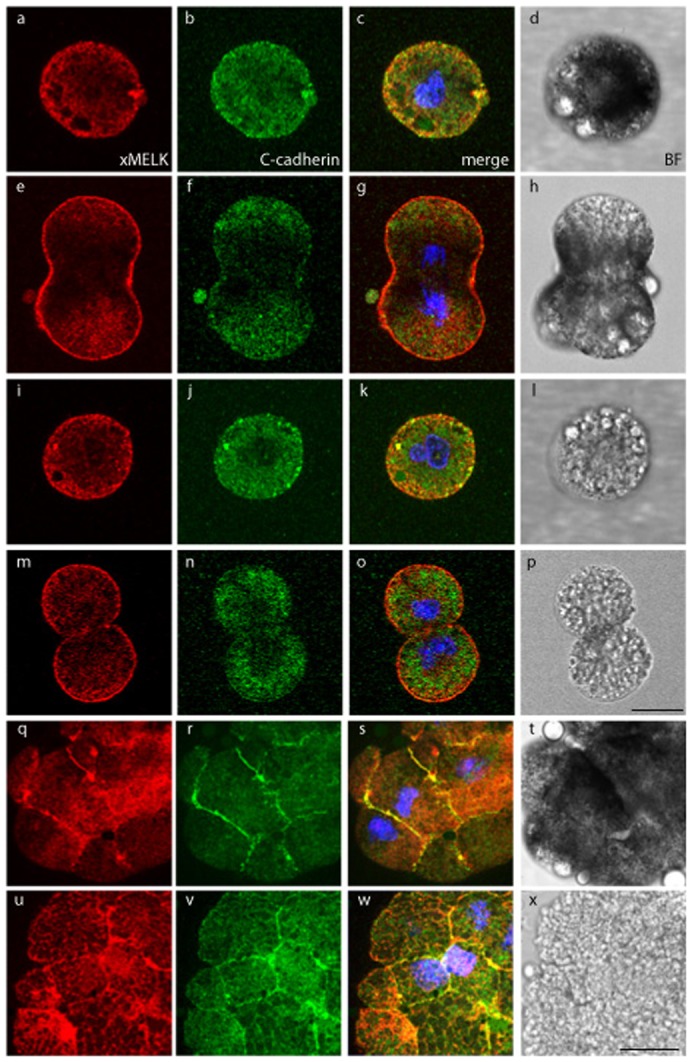
Animal caps of pigmented embryos were dissected and cells were dissociated with trypsin treatment. Cells were left isolated (a–p) or sorted according to their pigmentation and allowed to re-associate for 3 hours (q–x). Cells were fixed, processed for indirect immunofluorescence with anti-xMELK (red) anti-C-cadherin (green) antibodies and observed by confocal microscopy. Single optical sections are shown. Bright field (BF, grey) show pigmented epithelial cells (a–h,q–t) and mesenchyme-like cells devoid of pigment (i–p,u–x). Images were merged together with images of DNA (blue) at the same confocal plane to visualize co-localization of xMELK with C-cadherin (merge, c,g,k,o,s,w). Scale bars: 20 µm.
