Fig. 5. Model for the relationships between the RA, FGF and Notch pathway in Xenopus PSM.
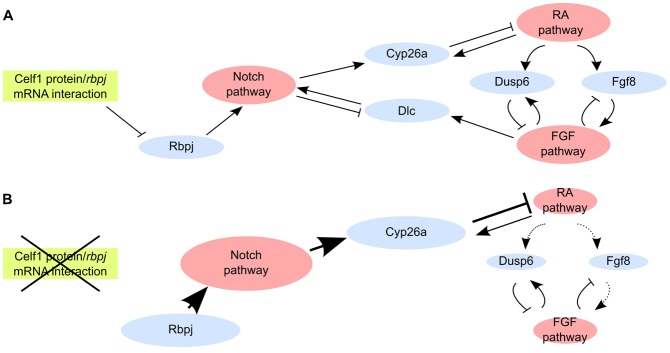
Three intra-pathway feedback loops attenuate each pathway (RA stimulate cyp26a and FGF stimulates dusp6 while Notch represses dlc). In addition, the RA pathway either stimulates (through fgf8) or represses (through dusp6) the FGF pathway, the FGF pathway stimulates the Notch pathway (through dlc), and the Notch pathway represses the RA pathway (through cyp26a). (A) The Celf1 RNA-binding protein attenuates the Notch pathway by limiting the abundance of Rbpj protein through a post-transcriptional control. Notch signalling depends on FGF signalling through Dlc. (B) When the TP MO impairs the repressive interaction between Celf1 and rbpj mRNA, rbpj is overexpressed, which stimulates the Notch pathway. Consequently, the RA pathway is repressed (due to cyp26a overexpression) and the FGF pathway is repressed (due to fgf8 repression). FGF repression does not lead to Notch repression owing to rbpj overexpression, and relieving the repressive interaction between Celf1 protein and rbpj mRNA uncouples the Notch and RA pathways from the FGF pathway.
