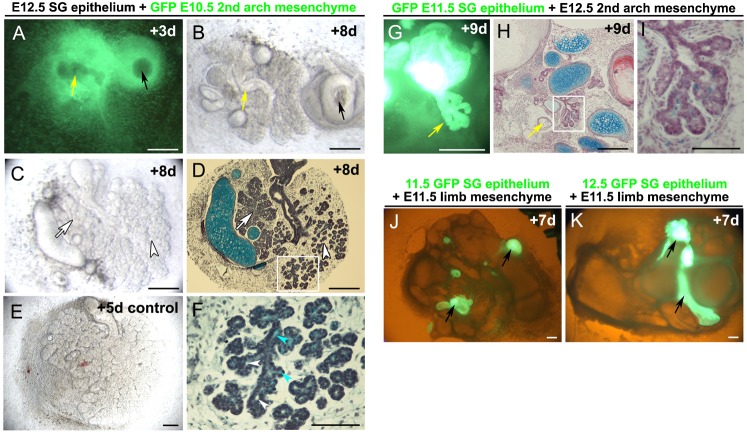
Fig. 2. Early gland epithelium drives salivary gland formation.
(A–D,F) E12.5 salivary gland epithelium combined with GFP labelled E10.5 2nd pharyngeal arch mesenchyme. (A) LHS Salivary gland epithelium (yellow arrow). RHS 2nd pharyngeal arch epithelium (black arrow) combined with GFP mesenchyme. Day 3. Dark field GFP. The non salivary gland epithelium remains as a rounded sphere while the salivary gland epithelium has started to elongate and a cleft has formed at the end of a bud-like structure. (B) Same culture after 8 days. The salivary gland epithelium has formed a classic branching structure with a central cavitated duct (yellow arrow), while the non-gland epithelium has formed a cyst (black arrow). (C) Salivary gland epithelium on second arch mesenchyme, cultured for 8 days. (D) Histology section of panel C. Two gland types are observed, mimicking the normal arrangement of the submandibular (arrowhead) and sublingual gland (arrow). (E) Control unrecombined salivary gland cultured from E12.5 for 5 days. (F) Magnification of boxed area in panel D, showing presence of developing lumens (white arrowheads) and alcian blue stained polysaccharides (blue arrows). (G–I) E11.5 GFP salivary gland epithelium combined with E12.5 2nd pharyngeal arch mesenchyme. (G) The epithelium attempts to make some extended branched structures after 9 days in culture (yellow arrow). (H) Histology section. Some branching structures with partially developed ductal lumens are evident after 9 days in culture. (I) Magnification of boxed area in panel H, showing alcian blue stained polysaccharides in the lumens. (J) E11.5 GFP salivary gland epithelium (arrows) combined with E11.5 limb mesenchyme after 7 days in culture. (K) E12.5 GFP salivary gland epithelium (arrows) combined with E11.5 limb mesenchyme after 7 days in culture. In both cases no branching structures form. Images smart sharpened in photoshop. Scales bars: 250 µm (A–E,G,H,J,K), 100 µm (I,F).