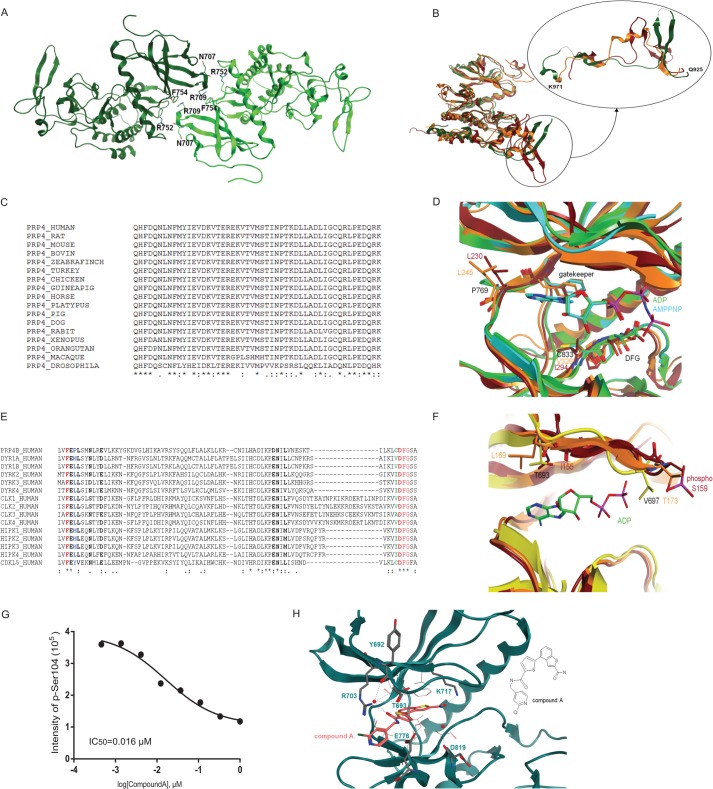
FIGURE 5.
PRP4 structural analysis. A, content of asymmetric unit. Apo-PRP4 chain A is shown in light green, and chain B is shown in dark green. Residues involved in potential H-bonds at the dimer interface are shown. Arg752 side chain NH2 and Phe754 main chain oxygen from one chain are involved with Asn707 main chain oxygen and Arg709 side chain NH2 from the other. B, overall superposition between apo-PRP4 (green; B chain), CLK2 (orange), and DYRK2 (red). The PRP4 kinase fold is similar to these homologues (left) with the exception of the PRP4 region 925–971 (see detail shown in a different orientation). PRP4 residues 936–939 and 961–962 could not be built because of poor electron density and are thus modeled with dashed lines. C, multiple sequence alignment (ClustalW (40)) of human PRP4 region 925–971 with diverse PRP4 sequences shows very high sequence conservation. D, structural alignment between PRP4 + ADP (green), PRP4 + AMPPNP (cyan), DYRK2 (red), and CLK2 (orange) show significant differences at the hinge 2 residues downstream of the gatekeeper and in front of the DFG motif. E, multiple sequence alignment (ClustalW) of human PRP4 region encompassing the hinge and the DFG motif with the closest homologous kinase domains. Residues shown in bold are located within 4.5 Å of the ligand based on the PRP4 + AMPPNP complex (chain A). The gatekeeper and the DFG are shown in red. The gatekeeper +2 is shown in blue. Pro769 in PRP4 at this position is highly unusual. The residue preceding the DFG is shown in green. Cys833 in PRP4 at this position is unusual as well. F, structural alignment between apo-PRP4 (yellow), DYRK2 (red), and CLK2 (orange). Detail of the differences at the G-rich loop is shown. Note that although the entire protein backbone could be built, Gln695 and Val697 were modeled as alanine due to the lack of clear electron density for the side chains. G, inhibition of PAK4 phosphorylation by Compound A. The effect of Compound A on PRP4 kinase activity was evaluated in a PAK4 biochemical assay. The assay was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The PAK4 peptide harboring Ser104 was identified and quantified by Orbitrap mass spectrometry. IC50 was obtained by fitting data to a four-parameter logistic equation. H, potential interactions between PRP4 and Compound A. Potential hydrogen bonds are shown with dashed lines. Note that not all hydrogen bonds that involve water and are close to the hinge can take place simultaneously. Residues involved in such interactions are shown in stick representation. Protein residues involved in potential hydrophobic interactions with benzothiophene of Compound A are depicted. The two-dimensional structure of Compound A is illustrated on the right for clarity. pSer, phosphoserine.