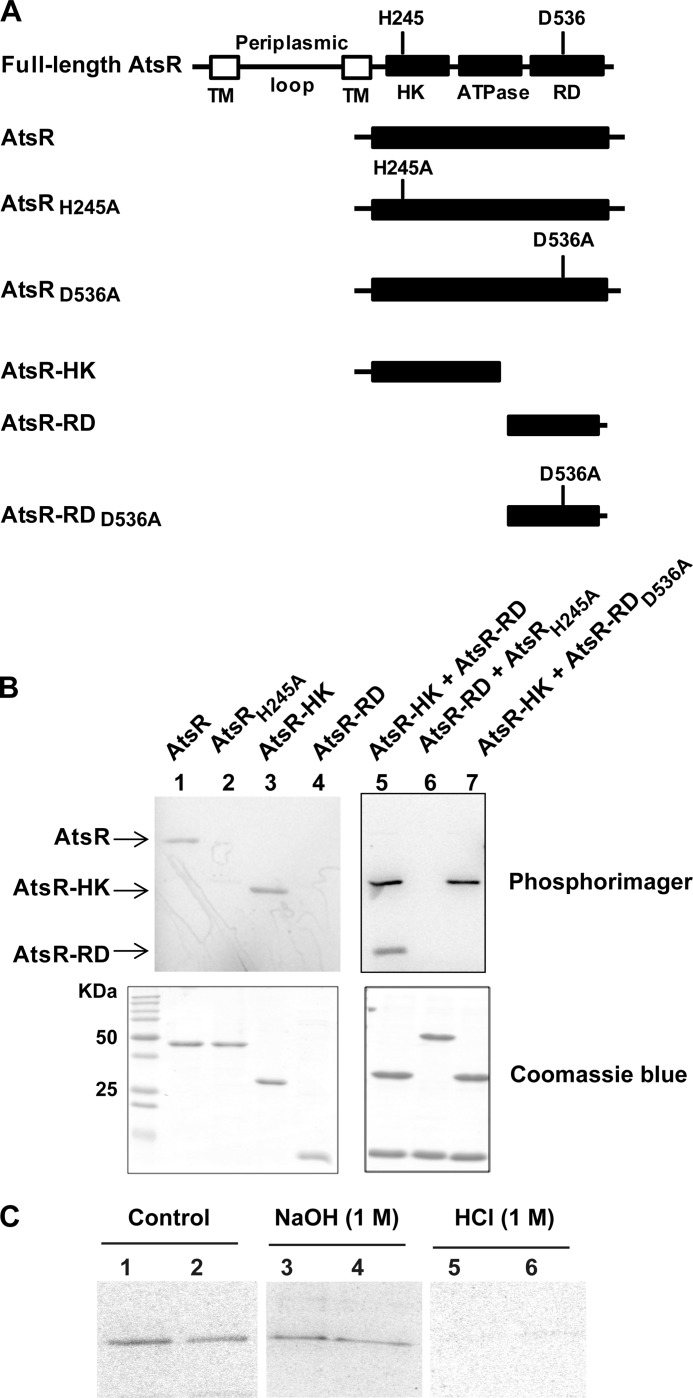
FIGURE 2.
Functional analysis of AtsR domains. A, schematic domain organization of AtsR and its derivatives (domains are not drawn to scale). The predicted sites of phosphorylation are His-245 (H245) and Asp-536 (D536). TM, transmembrane domain; HK, histidine kinase domain; ATPase, ATPase domain; RD, receiver domain; A, alanine. B, In vitro phosphorylation assays. Five μmol of purified AtsR, AtsRH245A, AtsR-HK, AtsR-RD, AtsR-HK and AtsR-RD, AtsRH245A and AtsR-RD, and AtsR-HK and AtsR-RDD536A were added in a standard phosphorylation mixture (100 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8, 50 mm KCl, 5 mm MgCl2, 1 mm DTT, 5 μCi [γ-33P]ATP) and incubated for 15 min at 25 °C. Reactions were terminated by adding 3× SDS-PAGE loading buffer and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The phosphorylated proteins were visualized using a PhosphorImager (top). Phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins were detected by Coomassie Blue staining (bottom). The location of phosphorylated bands of the AtsR, AtsR-HK, and AtsR-RD proteins are denoted with arrows. C, chemical stability of phosphorylated proteins. Phosphorylated AtsR (lanes 1, 3, and 5) and AtsRD536A (lanes 2, 4, and 6) were treated with 1 m NaOH or 1 m HCl or were left untreated for 45 min at room temperature. The reactions were neutralized with 0.25 volumes of 2 m Tris, pH 8, and analyzed by PhosphorImager after SDS-PAGE.