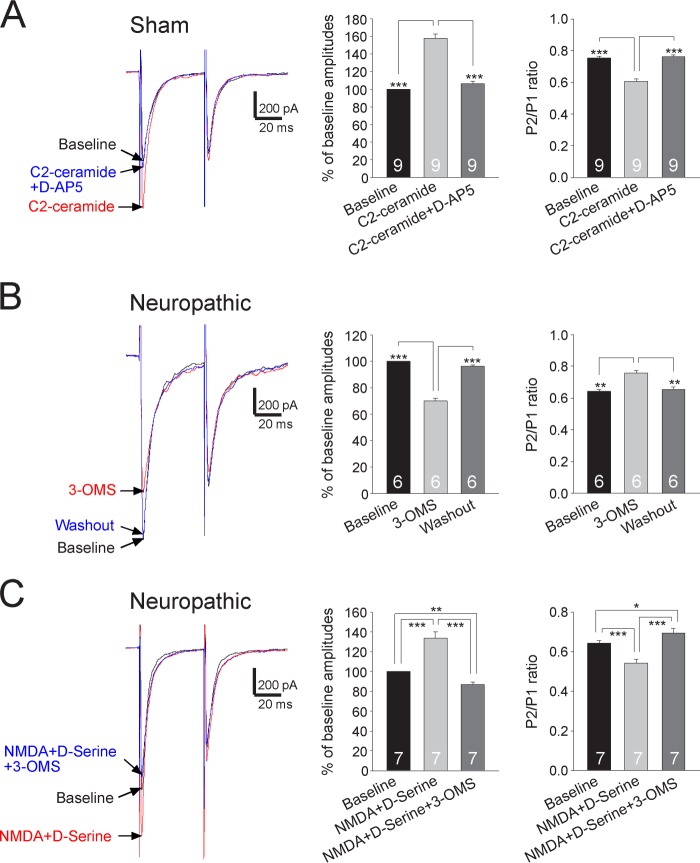
FIGURE 8.
Presynaptic NMDA receptors are effector receptors used by the sphingomyelinase/ceramide pathway to enhance glutamate release from the primary afferents in neuropathic rats. A, samples of EPSCs evoked by a pair of electrical pulses recorded from a neuron of sham-operated rats at base line, during perfusion of C2-ceramide (2 μg/ml), and then during addition of the NMDA receptor inhibitor D-AP5 (25 μm) in the presence of C2-ceramide. B, samples of EPSCs evoked by a pair of electrical pulses recorded from a neuron of neuropathic rats at base line, during, and after washout of the neutral sphingomyelinase inhibitor (3-OMS, 30 μm). C, samples of EPSCs evoked by a pair of electrical pulses recorded from a neuron of neuropathic rats at base line, during perfusion of NMDA (50 μm) plus d-serine (200 μm), and then during addition of 3-OMS (30 μm) in the presence of NMDA plus d-serine. Bar graphs (right) show the mean percentage (+S.E.) of base-line amplitude and mean (+ S.E.) P2/P1 ratios for the tested agents. The number of neurons included in each group for the analysis is shown in each bar. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.