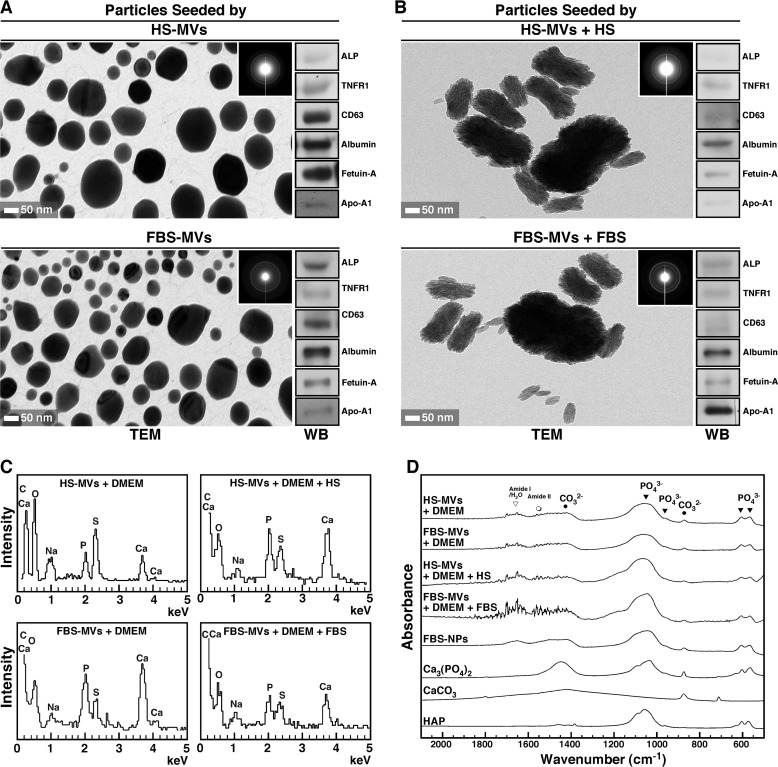
FIGURE 4.
MV-induced mineral precipitation represents calcium phosphate mineralo-organic NPs. A, mineral precipitates obtained from DMEM containing MVs as in Fig. 3A were harvested by centrifugation and analyzed by TEM without fixation or staining. The precipitates displayed round NPs with a dark electron-dense structure. The polycrystalline, mineralized nature of the particles was confirmed by the concentric rings produced on electron diffraction patterns (insets). Western blotting analysis revealed the presence of MV-associated proteins within the seeded mineralo-organic NPs (right panels). B, mineral precipitates obtained from DMEM containing both MVs and 5% serum showed ellipsoid NPs of a polycrystalline nature (insets). MV-associated proteins were also detected in these particles (right panels). C, EDX spectra of mineral particles seeded by MVs with or without 5% serum showed peaks corresponding to carbon, calcium, oxygen, sodium, phosphorus, and sulfur. D, FTIR analysis revealed the presence of both phosphate groups at 566, 604, and 960 cm−1 and between 1,033 and 1,100 cm−1 and carbonate at 875 and 1,430 cm−1, consistent with the presence of carbonate apatite. Peaks corresponding to water and the amide bonds of proteins were also observed in MV-seeded particles. Mineralo-organic NPs prepared by adding 1 mm CaCl2 and NaH2PO4 each in 1 ml of DMEM containing 5% FBS showed similar peaks (FBS-NPs). Commercial powders of Ca3(PO4)2, CaCO3, and HAP were included for comparison. WB, Western blot.