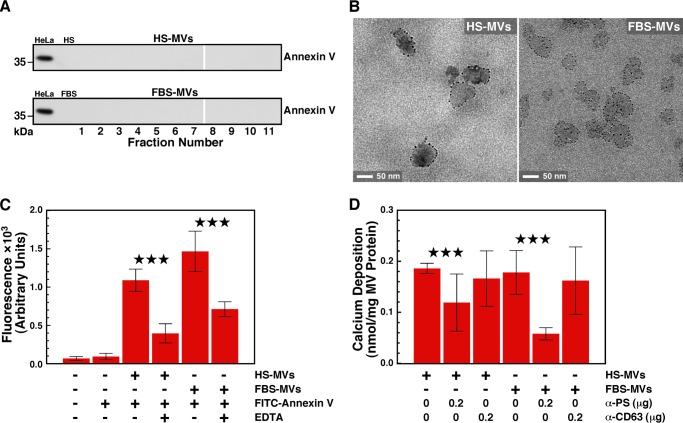
FIGURE 5.
PS exposed on the surface of serum MVs contributes to seeding of mineralo-organic NPs. A, Western blotting showing the absence of annexin V on MVs isolated from either HS or FBS by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Equal amounts of proteins (60 μg) from either HeLa cell lysates (positive control), whole serum, or MV fractions (corresponding to the same fractions as in Fig. 2) were separated under denaturing and reducing conditions on SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-annexin V antibody. B, annexin V-immunogold labeling of serum MVs. Fixed and stained thin sections of MVs were treated sequentially with annexin V, rabbit anti-annexin V antibody, and gold-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody prior to observation by TEM. Binding of the gold particles to MVs revealed the presence of PS on the vesicles' surface. C, annexin V-fluorescence labeling of serum MVs. MVs corresponding to 30 μg of total protein content were incubated for 30 min at room temperature with FITC-labeled annexin V in 100 μl of HEPES buffer prior to centrifugation and washing steps. Both HS-MVs and FBS-MVs produced fluorescence, which was abrogated by the calcium chelator EDTA (0.5 mm). Reaction mixtures containing either no reagents or FITC-annexin V alone were processed as above and used as negative controls. D, PS contributes to MV-induced mineral seeding. MVs (2 mg of total proteins) were treated with either anti-PS or anti-CD63 antibody (0.2 μg/ml) for 1 h at room temperature. MVs were then pelleted, washed, and incubated in DMEM for 1 week before measuring calcium deposition. ***, p < 0.01. Error bars, S.E.