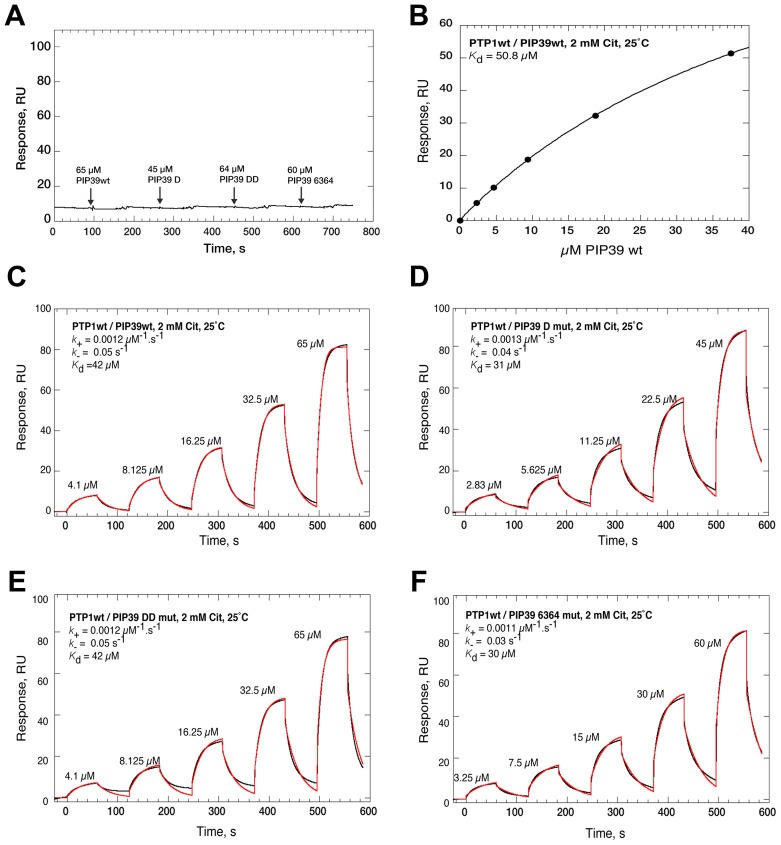
Figure 8. Characterisation of the interaction of TbPTP1 with TbPIP39 (wild type and mutants), in the presence or absence of citrate using BIAcore T200.
A. Representative double reference corrected single cycle kinetic titration SPR binding curves (black), monitored on a surface of covalently stabilized His-PTP1wt, for TbPIP39wt (65 µM), TbPIP39 D mutant (45 µM), TbPIP39 DD mutant (64 µM) or TbPIP39 6364 mutant (60 µM) at 25°C in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4; 150 mM NaCl; 0.05% P20; 2 mM DTT; 20 mM MgCl2 in the absence of citrate. B. Steady state analysis of the interaction between TbPTP1 and TbPIP39 by surface plasmon resonance. The assay was run in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4; 150 mM NaCl; 0.05% P20; 2 mM DTT; 20 mM MgCl2; 2 mM citrate. A concentration dependent interaction between TbPTP1wt and TbPIP39wt was seen. All fits were to a 1∶1 binding model, with mass transport considerations. Kd is ∼40–50 uM. C–D Representative double reference corrected single cycle kinetic titration SPR binding curves (black), monitored on a surface of covalently stabilized His-PTP1wt, for TbPIP39wt (C), TbPIP39 D mutant (D), TbPIP39 DD mutant (E) or TbPIP39 6364 mutant (F) at 25°C in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4; 150 mM NaCl; 0.05% P20; 2 mM DTT; 20 mM MgCl2 with 2 mM citrate. In each case, a three-fold dilution series of TbPIP39 (wild type and mutants) was injected over the surface, at 30 µl.min-1 and the apparent on- and off-rate constants were by globally fitting (red) a 1∶1 kinetic binding model, with mass transport considerations, to the sensorgrams using the analysis software (v1.02, GE Healthcare) supplied with the instrument.